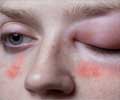
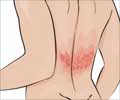
New oral drug BCX7353 may lower the rate of attacks of hereditary angioedema, a rare genetic disorder characterized by recurrent painful swellings of the skin and mucous membranes. Side effects may include mild gastrointestinal symptoms.
- BCX7353 may lower the rate of attacks of hereditary angioedema.
- BCX7353 is a new drug that is administered orally as a capsule.
- Hereditary angioedema is a rare genetic disorder characterized by recurrent painful swellings of the skin and mucous membranes.
Genetic disorder leads to uncontrolled swellings
For most cases of hereditary angioedema, the underlying cause is a congenital deficiency or dysfunction of what is known as C1-inhibitor. As a result of C1-inhibitor deficiency, plasma levels of bradykinin increase, a peptide which locally increases the permeability of the smallest blood vessels.
The central role of bradykinin in the development of angioedema attacks is well established for hereditary angioedema. Attacks of angioedema in patients with hereditary angioedema are related to the action of bradykinin, whose generation is closely linked to another plasma protein, called kallikrein. If kallikrein is active, then bradyinin generation is the result. The inhibition of kallikrein should therefore be a suitable measure for prophylaxis of angioedema attacks.
Therapeutic breakthrough in the form of capsules
So far, the prevention of angioedema attacks in hereditary angioedema was bound to medication that required injections. Although drugs were also available as tablets, these proved either ineffective or were not licensed in many countries. In addition, some of them led to severe side effects and could not be administered to children or during pregnancy.
The new drug BCX7353 tested in the study is a synthetic small molecule that acts as a specific kallikrein inhibitor and is administered as capsules. The aim of the development was to achieve an effective prophylaxis with the distinct advantages of an oral administration yet without the side effects of the oral preparations used previously.
During the study, 77 patients were randomized to groups of four different dose levels or placebo. They took the respective dose once daily for 28 days. The patients noted in their diaries the frequency, localization and severity of the attacks; quality of life was recorded at the beginning and the end of the study using a validated questionnaire. Changes in the frequency of the attacks were investigated, as were the side effects from the treatment and the impact on patients' quality of life.
Convincing results
The results were positive: With a daily dose of 125 mg and higher, a significant reduction of angioedema attacks was demonstrated. Patients who took 125 mg of BCX7353 per day even experienced a reduction in the frequency of their attacks of almost 75 percent compared to placebo; over 40 percent of patients in that dose group remained completely free of attacks during the study. Also the increase in quality of life was most evident for the 125 mg dose; in addition, not only the number of peripheral attacks was reduced in this group but also those in the gastrointestinal tract. Moreover, the side effects of this dose ranged mild.
References:
- Oral Plasma Kallikrein Inhibitor for Prophylaxis in Hereditary Angioedema - (https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa1716995)
Source-Eurekalert