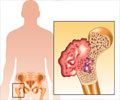
Painkillers prescribed to reduce pain may stop the beneficial effects of bone-protective drugs called bisphosphonates.
“We need to exercise some caution in extrapolating these data to more widely used bisphosphonates in osteoporosis, but given that concomitant usage of NSAIDs and bisphosphonates is relatively common, this could have major clinical consequences and result in a failure to reduce fracture risk as much as we had hoped,” said senior author Eugene McCloskey, MD, of Northern General Hospital, in the UK.
Source-Eurekalert