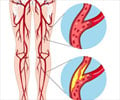
The disease is responsible for impaired blood flow and leg pain, according to a recent research.
Peripheral artery disease can be delayed to a great extent by taking walks thrice a week. The disease is responsible for impaired blood flow and leg pain, according to a recent research. The walking ability of a person can also be improved through the exercise. As a part of the study, researchers tested the physical ability of 417 men and women by measuring the distance they could walk in 6 minutes and by observing their ability to get up from a chair unassisted. They also studied how well the participants maintained balance in a standing position, and how fast they could walk over a short distance.
The researchers found that as per the study, people who walked for exercise three or more times per week had a significantly smaller average annual decline in walking distance and speed than those who walked one to two times per week.They also noted a disparity in the amount of exercise between people of different races. The researchers realized that only a small proportion of African-American study participants walked for exercise three or more times per week. Previous studies have shown that African-American patients with peripheral artery disease have greater functional impairment than white patients, and that the prevalence of the disease is higher in African-Americans than in white patients.
Mary McGrae McDermott, M.D., associate professor of medicine, division of general internal medicine, at the Feinberg School who led the study, said that the data suggested that doctors should encourage African-American patients to get more exercise.
'Data from the study suggest that doctors should take steps to encourage African-American individuals to increase their frequency of walking exercise,' she said.
The study was conducted by researchers at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and is published in January issue of the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Edited (ANI)