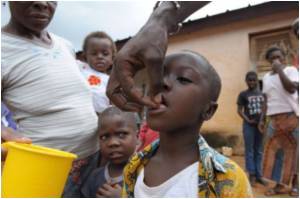
River blindness, or onchocerciasis, is a disease caused by a parasitic worm found primarily in Africa. The parasite is spread by the bites of infected black flies that breed in rapidly flowing rivers.

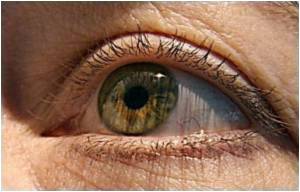
‘River blindness has affected countries in Africa and Latin America, as well as Yemen. The disease can cause intense itching, eye damage, and irreversible blindness, reducing an individual's ability to work and learn.’





In a paper published in the New England Journal of Medicine, scientists from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, and other organizations describe how a cell phone-based videomicroscope can provide fast and effective testing for L. loa parasites in the blood, allowing these individuals to be protected from the adverse effects of ivermectin. In the new study, 16,259 volunteers in 92 villages in Cameroon where both L. loa and O. volvulus are commonly found provided finger-prick blood samples. These samples were then tested for L. loa using the LoaScope, a small microscope that incorporates a cell phone. Developed by a team led by researchers from NIAID and the University of California, Berkeley, the LoaScope returns test results in less than three minutes.
Volunteers who were not infected or who had low-level L. loa infections were given standard ivermectin treatment and observed closely for six days afterwards. Volunteers with high numbers of L. loa parasites in their blood did not receive ivermectin.
Using this strategy, 15,522 study volunteers were successfully treated with ivermectin without serious complications. Nearly 1,000 participants experienced mild adverse effects following ivermectin treatment. According to the study authors, the LoaScope could be a valuable approach in the fight against river blindness by effectively targeting populations for ivermectin treatment, and protecting dually-infected patients from complications of inadvertent ivermectin administration.
Source-Eurekalert