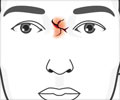
Emergency departments prefer administering medicines through the nasal route compared to IV injections, because of its convenience.
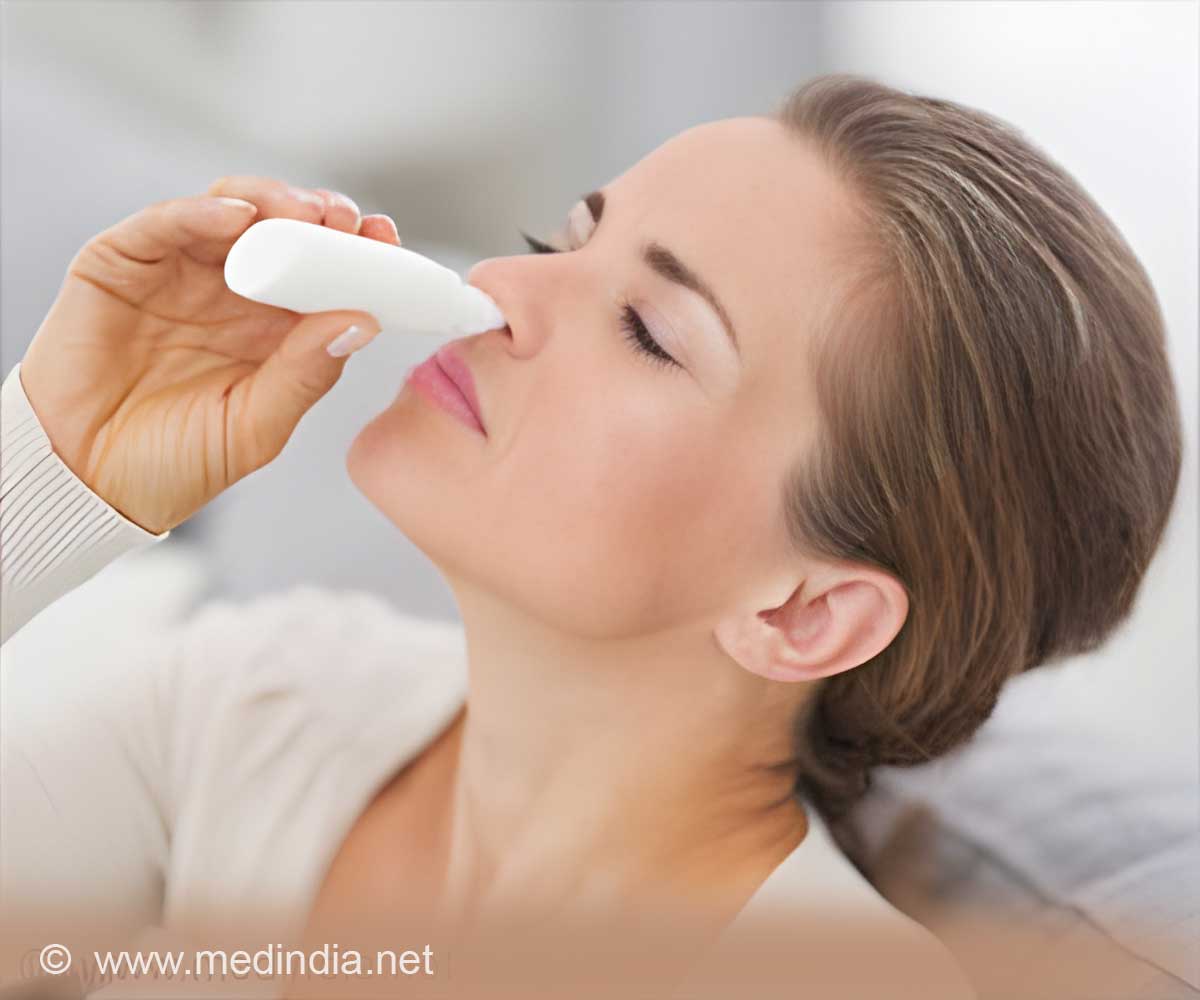

‘The intranasal route of medicine administration does not require needles, it is less painful, easy and non-invasive. It minimizes the spread of infectious diseases and ensures faster delivery of medication to the bloodstream.’





To administer a medication through the nose, a nurse or physician attaches a device called an atomizer to a syringe. The device then is placed in the patient's nostril. When the syringe plunger is pushed, a fine mist of medication covers the inside surface of the nose, providing a shortcut to the brain.The intranasal route requires no needles, is less painful than IVs or injections and minimizes the spread of infectious diseases. For certain patients, including children, the elderly and the obese, the intranasal route also can deliver a medication to the bloodstream more quickly than an injection.
In some patients, IVs and injections are difficult to administer. A patient may be seizing or combative. An IV drug user may have collapsed veins. A child may be afraid of needles. A patient may be wearing multiple layers of clothes. Or it may be difficult and time consuming to obtain an intravenous line.
The review article by Rech and colleagues examined intranasal administration of five common medications used in emergency departments: midazolam (used to tranquilize and sedate children and treat seizures in children and adults); fentanyl (for pain relief); naloxone (for opioid overdoses); ketamine (to induce anesthesia) and dexmedetomidine (to sedate and relieve pain in children).
Previous research has found that, when administered intranasally, midazolam is effective for procedural sedation, anxiety and seizures and fentanyl is safe and effective for managing acute pain. The intranasal route also appears to be an effective alternative for naloxone for opioid overdose. The research to date is less clear on the roles for intranasal ketamine and dexmedetomidine.
Advertisement
The paper is titled, "When to Pick the Nose: Out-of-Hospital and Emergency Department Intranasal Administration of Medications."
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert