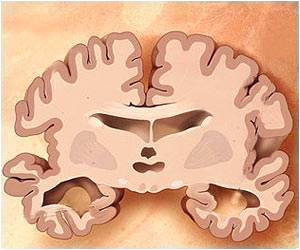
A new potential target in the fight against Alzheimer's and other neurodegenerative diseases has been identified by a team of scientists.

Kosik and his research team focused on tau, a protein normally present in the brain, which can develop into neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) that, along with plaques containing amyloid-ß protein, characterize Alzheimer's disease. When tau becomes pathological, many phosphate groups attach to it, causing it to become dysfunctional and intensely phosphorylated, or hyperphosphorylated. Aggregations of hyperphosphorylated tau are also referred to as paired helical filaments.
Source-Eurekalert