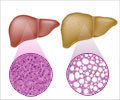
Researchers at Johns Hopkins have used specialized 3-D MRI scans to precisely measure living and dying tumor tissue in a series of studies involving 14 American men and women with liver tumor tissue.
They also say their results – in patients with either primary liver cancers or metastatic tumors from cancers originating elsewhere in the body -- are evidence that using this technology before and after treatment is a faster and better tool for predicting patient survival after chemotherapy targeted directly at tumors, called chemoembolization.
Unlike standard methods to assess tumor response after chemoembolization, which are based on two-dimensional images and tumor size, the Johns Hopkins-developed 3-D technology also distinguishes between dead and live tissue, giving an accurate assessment of tumor cell death.
The new technology builds on standard 2-D methods and uses computer analytics to evaluate the amount of so-called contrast dye absorbed by tumor tissue. The dye is injected into patients before their MRI scan to enhance image production. Researchers say live tissue will absorb more dye than dead tissue, affecting image brightness, which can also be measured for size and intensity.
"Our high-precision, 3-D images of tumors provide better information to patients about whether chemoembolization has started to kill their tumors so that physicians can make more well-informed treatment recommendations," says Johns Hopkins interventional radiologist Jean-Francois Geschwind, M.D., the senior investigator on the studies.
Geschwind, a professor in the Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and its Kimmel Cancer Center, says that knowing the true extent of a tumor's response to chemoembolization is particularly important for patients with moderate to advanced stages of the disease, whose liver tumors might initially be too large or too numerous to surgically remove.
Advertisement
In a series of additional studies, Geschwind and his team used the standard and new imaging techniques to analyze the MRI scans of more than 300 liver tumors in some 123 other men and women, also from the Baltimore region. All patients were treated at The Johns Hopkins Hospital between 2003 and 2012, and each received pre- and post-chemoembolization MRI scans to assess the effects of therapy on the tumors.
Advertisement
Geschwind says the 3-D technology's improved accuracy removes a lot of the guesswork that now goes into evaluating treatment outcomes. The new assessment takes seconds to perform, he adds, so radiologists can provide faster, almost instantaneous treatment advice.
Geschwind and his team plan further software refinements to the new approach before training more physicians to use it. He also has plans to study how it can affect treatment decisions, and whether these therapy choices help people live longer.
The software used in the MRI scans was developed at Johns Hopkins and at Philips Research North America, in Briarcliff Manor, N.Y. Philips, whose parent company is based in the Netherlands, manufactures some of the MRI devices used in the study.
Liver cancer kills nearly 20,000 Americans each year, and is much more prevalent outside the United States, where it is among the top-three causes of cancer death in the world. Experts cite the rising numbers of hepatitis C infections, which cause chronic liver inflammation and are a leading risk factor for liver cancer.
Source-Eurekalert