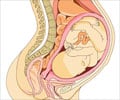
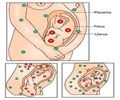
Fetal growth restriction impacts around 60,000 infants annually in Europe and the United States.
Maternal PlGF and umbilical Dopplers predict pregnancy outcomes at diagnosis of early-onset fetal growth restriction
Go to source). The research, published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, involved 142 women from the //EVERREST Prospective Study (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Does Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Gene Therapy Safely Improve Outcome in Severe Early-Onset Fetal Growth Restriction? (EVERREST)
Go to source) who had severe early-onset fetal growth restriction (FGR) – meaning their babies were very small on ultrasound scans early in the second half of pregnancy (between 20 and 27 weeks).
‘By evaluating ultrasound and protein measurements, both independently and in combination, researchers could predict stillbirth, neonatal death, and extreme preterm delivery before 28 weeks of pregnancy. #pretermbirth #stillbirth #fetalgrowth #pregnancycomplications’





Some babies with FGR continue to grow and are born around their due date. However, many will either need extreme preterm delivery (before 28 weeks of pregnancy) or will not survive the pregnancy, resulting in stillbirth. In England alone, it is estimated that the annual total costs of neonatal care are £262million (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Neonatal health care costs of very preterm babies in England: a retrospective analysis of a national birth cohort
Go to source).
Lead author, Dr. Rebecca Spencer (UCL EGA Institute for Women’s Health (4✔ ✔Trusted Source
EGA Institute for Women's Health
Go to source) and University of Leeds), said: “There is currently a lot of uncertainty for the families of unborn babies with early-onset fetal growth restriction and for their health-carers."
“We want to give them a better idea of what to expect if they are affected – as many people find uncertainty harder to cope with than definite bad news."
Enhancing Pregnancy Outcome Predictions to Guide Ultrasound Frequency
“Predicting pregnancy outcomes may also help doctors decide how often to do ultrasound scans and when to give antenatal steroids to prepare the baby for preterm delivery.”Results were analysed for 123 women who had provided blood samples and had regular ultrasound examinations of their baby’s size and wellbeing.
Advertisement
The team asked both women and their doctors about which pregnancy outcomes they thought were important to them, these included:
- Fetal or neonatal death.
- Death or delivery before 28 weeks.
- Development of abnormal umbilical artery Dopplers (a marker of placental insufficiency which can lead to fetal growth restriction or preterm delivery).
- Delivery at 37 weeks or more.
Advertisement
Senior author, Professor Anna David (UCL EGA Institute for Women’s Health) leads the multinational EVERREST consortium. The EVERREST consortium is developing a novel treatment to improve the growth and outcomes of very small babies in the womb.
Professor David said: “Currently we have no therapy to improve fetal growth inside the womb but a novel drug is being developed by our team. This will need to be tested in clinical trials. These results will help researchers to identify those women who might be most suitable to participate in the clinical trial, where the possible benefits outweigh the risks.
“Better prediction of which pregnancies will end in stillbirth, neonatal death or extreme preterm delivery will help to identify who should be included in these trials.”
References:
- Maternal PlGF and umbilical Dopplers predict pregnancy outcomes at diagnosis of early-onset fetal growth restriction - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37712421/)
- Does Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Gene Therapy Safely Improve Outcome in Severe Early-Onset Fetal Growth Restriction? (EVERREST) - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26086754/)
- Neonatal health care costs of very preterm babies in England: a retrospective analysis of a national birth cohort - (https://bmjpaedsopen.bmj.com/content/7/1/e001818#DC1)
- EGA Institute for Women's Health - (https://www.ucl.ac.uk/womens-health/ega-institute-womens-health)
Source-Eurekalert