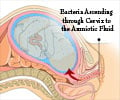
Pregnant women with Sjogren's or lupus syndrome have elevated anti-Ro/SSA antibodies which are linked to fetal atrioventricular block in the heart.
Prospective Evaluation of High Titer Autoantibodies and Fetal Home Monitoring in the Detection of Atrioventricular Block Among Anti-SSA/Ro Pregnancies
Go to source).
Pregnancy Sjogren’s & Lupus Syndrome Linked to Fetal Heart Disease
Some individuals with anti-Ro/SSA antibodies (anti–Sjögren's-syndrome-related antigen A autoantibodies, also called anti-Ro antibodies) have autoimmune diseases such as lupus or Sjögren's syndrome, but many have no symptoms.‘Antibodies detection in autoimmune diseases like Sjogren’s or lupus syndrome in pregnancy could potentially help to streamline fetal cardiac monitoring for high-risk individuals. #pregnancy #autoimmunedisease #sjogrensyndrome #lupussyndrome #fetalAVblock #hearthealth’





In the trial, called Surveillance To Prevent AV Block Likely to Occur Quickly (STOP BLOQ), the incidence of AVB increased with higher levels of anti-Ro/SSA antibodies, reaching 7.7% for those in the top quartile, which increased to 27.3% in those with a previous child who had AVB, although participant numbers in that category were small. Antibody titers did not change over time. The trial also revealed that home-based fetal heart rate monitoring reliably detected conduction abnormalities, which may reduce the need for serial echocardiograms.“Examining the levels of anti-Ro/SSA antibodies is an important advance since for women with low titers, monitoring is probably not necessary and for those with high titers the increased risk supports surveillance,” said corresponding author Jill Buyon, MD, of NYU Langone Health. She added that this study also indicated that titers of antibodies do not change and that additional factors besides antibodies contribute to risk.
“That home monitoring can rapidly and accurately identify early fetal conduction disease is a major step forward that may significantly decrease the need for echocardiograms and hopefully facilitate reversibility,” added senior author and research professor Bettina Cuneo MD, of the University of Arizona-Tucson College of Medicine.
Reference:
- Prospective Evaluation of High Titer Autoantibodies and Fetal Home Monitoring in the Detection of Atrioventricular Block Among Anti-SSA/Ro Pregnancies - (https://acrjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/art.42733)
Source-Eurekalert