Scientists of University of Washington in Seattle have devised a simple blood test, which can be used to detect rare disorders of progressive genetic diseases known as 'lysosomal storage disorders'
Scientists of University of Washington in Seattle have devised a simple blood test, which can be used to detect rare disorders of progressive genetic diseases known as 'lysosomal storage disorders', according to online edition of Nature.
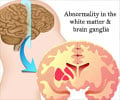
These disorders can cause symptoms ranging from gross enlargement of the liver to mental retardation. Some 40-50 of the disorders are known, and in total they affect one in 5,000 people. Gaucher disease, one of the more common afflictions, affects a little more than one in 1,000 Ashkenazi Jews.The researchers say their screening method can now detect seven of these diseases. Cambridge-based company Genzyme, which sells treatments for three of the diseases, hopes to see the screen made a routine part of newborn testing.
Lysosomes are small compartments within cells that help to recycle waste cellular material within the body. Enzymes within the lysosomes do this job by breaking up waste materials into smaller pieces.
If one of these enzymes is not functioning, usually because of a problem in the gene that codes for it, then the breakdown stops and half-digested matter clogs up the cell with disastrous consequences.
Newborn babies with these diseases can be healthy, because there has been little time for this material to build up. Blood tests are available for cases where lysosomal diseases are suspected.
But doctors are keen to find a way to diagnose the disorders before problems begin so that treatment, if it exists for the specific condition, can start early.
Advertisement
The methodology by them isn't very complicated and should be quite cheap, researchers said. The group estimates that a single machine should be able to process 85,000 screenings a year.
Advertisement
--Edited IANS