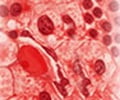
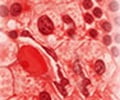
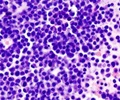
Prolonging the formula feeding and delaying the introduction to solid foods may put the child at risk of developing acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Schraw and colleagues surveyed 284 controls and 142 children from the Texas Children's Cancer Center and the National Children's Study in Houston, San Antonio and Austin, Texas, who had been diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Compared with controls, children diagnosed with ALL started solid foods significantly later, more of their mothers smoked during pregnancy and they had a longer duration of formula feeding.
Researchers found that the risk for developing ALL increased by 16 percent for every month of formula feeding. In addition, for each month the introduction of solid foods was delayed, the risk increased by 14 percent.
"One explanation for this co-risk may be that it's the same effect being picked up twice," said Schraw. "Children being given solid foods later may be receiving formula longer." Future research should address the factors influencing prolonged formula feeding and delay in solid food introduction, according to the researchers.
Source-Newswise