Researchers have found that EAAC1 protein helps in Cysteine transfer into neurons that helps in free radical scavenging
EAAC1 protein was found to be responsible for transferring the amino acid Cysteine into neurons, which is very important for reducing oxidative stress as Cysteine present in glutathione is responsible for it’s free radical scavenging activity in brain. Free radicals are responsible for causing diseases, which is scavenged by antioxidants. Professor Raymond Swanson and his team from Neurology and Rehabilitation services, San Francisco VA Medical Center have identified the usefulness of proteins EACC1 in Mice and EAAT3 in humans which are responsible for transfer of Cysteine to neuron cells.
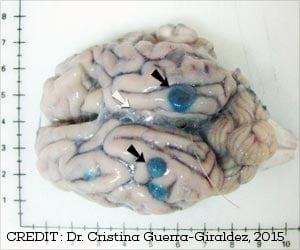
The researchers conducted their study in EAAC1 gene deficient mice and compared their physical characters and behavior with normal mice and found that the EAAC1 gene deficient mice had a retarded growth, enlarged ventricles and was found to be under stress. The researchers are finding out the difference of EAAC1 expression in Neuro-degenerative diseases.Source: Eurekalert.