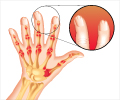
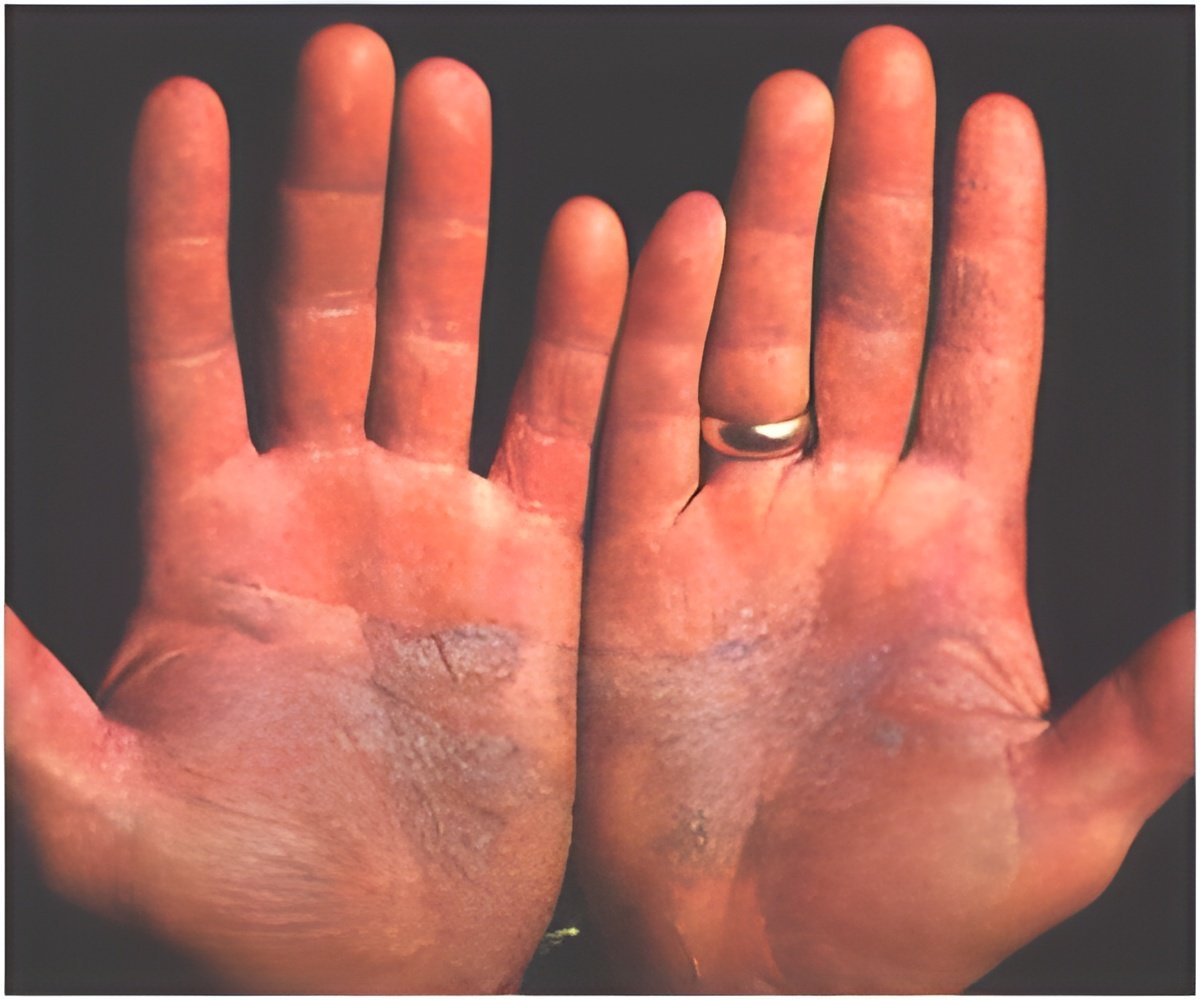
Psoriasis patients turn to complementary therapy because what was initially prescribed is not working out for them.
‘Proper educational initiatives should be taken to enable physicians to discuss evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine to improve patient satisfaction and outcomes.’
Read More..




Treatments for psoriasis range from topical ointments to ultraviolet light therapy to drugs. Psoriasis is associated with other serious conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and depression.Read More..
Through a survey distributed by the National Psoriasis Foundation, a team led by Adam Friedman, MD, interim chair of the Department of Dermatology at the GW School of Medicine and Health Sciences, found that patients with psoriasis typically turned to complementary or alternative medicine when their traditional medications failed or presented harsh side effects.
"Patients turn to these treatments because what was initially prescribed is not working out for them," explained Friedman. "But what we found through the survey is that patients may not completely understand what products will work best for them."
The survey found that patients reported using complementary and alternative medicine that have not previously exhibited efficacy or have not been studied for the treatment of psoriasis. Vitamins D and B12 were frequently reported, though neither of which have documented efficacy against the disease.
In contrast, indigo naturalis -- a plant extract widely used in Traditional Chinese Medicine and recognized as a therapy for several inflammatory conditions -- has shown efficacy, but was not reported in the survey. Dead Sea treatments were commonly reported and have shown therapeutic benefit.
Advertisement
Acknowledging that these treatments are part of patients' armament, Friedman and his team suggest that educational initiatives that enable physicians to discuss evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine may improve patient satisfaction and outcomes.
Source-Eurekalert