Researchers from Toronto have said that combined assessment of parathyroid hormone along with vitamin D may be needed to gauge the impact of vitamin D status on sugar metabolism.
The new findings might explain why studies of vitamin D alone have been conflicting and why clinical trials of vitamin D supplementation to improve diabetes have been disappointing, says principal investigator Dr. Ravi Retnakaran. He is a clinician-scientist at the Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute at Mount Sinai Hospital in Toronto, where he is an endocrinologist in the hospital's Leadership Sinai Centre for Diabetes and associate professor in the Department of Medicine at University of Toronto.
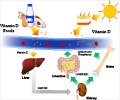
It is well known that, in response to low vitamin D levels, the body increases secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH), which is its upstream regulator. Dr. Retnakaran and co-authors show that glucose levels are perturbed only when low vitamin D is accompanied by increased PTH.
Supplementation across the board is not warranted:
The study findings suggest that patients with normal PTH are unlikely to benefit from vitamin D (25-OH-D) supplementation since their glucose handling is normal. Specifically, it may be that glucose metabolism is only adversely affected when circulating 25-OH-D falls to a level that causes PTH to rise, reflecting true functional vitamin D inadequacy.
In other words, not all patients with low vitamin D behave in the same manner. Only those also showing increased PTH appear to be at risk for pre-diabetes and diabetes. For that reason, research on vitamin D in diabetes should focus on patients with low vitamin D and increased PTH.
Advertisement
Observational study of 494 women:
Advertisement
Notably, 32% of those with pre-diabetes or diabetes at 12 months postpartum had had both vitamin D deficiency and PTH in the highest tertile at three months postpartum. Similarly, on multiple linear regression analyses, vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency with PTH in the highest tertile at three months independently predicted poorer beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity, and increased fasting and two-hour glucose at 12 months postpartum. In contrast, vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency with lower PTH did not predict these outcomes.
These findings support an effect of vitamin D status on glucose homeostasis by demonstrating an independent role of the PTH-vitamin D axis in the development of dysglycemia, insulin resistance, and beta-cell dysfunction.
Most importantly, these data highlight the need for assessment of the entire PTH/25-OH-D axis when studying the effect of vitamin D on glucose metabolism. This concept may partly explain the conflicted literature to date and has implications for future clinical trials examining the impact of vitamin D supplementation on pre-diabetes and diabetes.
Source-Eurekalert