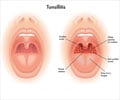
Adenotonsillectomy is a common procedure in children , even though evidence of its benefits is lacking in cases with milder symptoms. A new study
Adenotonsillectomy is a common procedure in children , even though evidence of its benefits is lacking in cases with milder symptoms. A new study suggests there are no major benefits to surgically removing tonsils and adenoids in children with mild throat infections.
Researchers examined 300 children, ages 2 to 8, with recurrent throat infections or enlarged tonsils and adenoids. Half of the children had the surgery, and half were allocated to watchful waiting. Within six months of surgery, the number of fevers, throat infections and upper respiratory tract infections was marginally reduced. However, between the six- and 24-month follow-ups, there was no difference between the groups.Thus researchers conclude that adenotonsillectomy has no major benefit over watchful waiting in children with mild throat symptoms. They add that these results can only be generalized for this specific subgroup with mild symptoms. Surgery is considered beneficial for children with frequent throat infections and obstructive sleep apnea.