A study published by Cell Press on November 20 in the Biophysical Journal provides new insights into what causes uncontrollable bleeding in hemophilia patients.
"Disorders of blood coagulation are a leading and immediate cause of mortality and morbidity in the developed world," says senior study author Fazoil Ataullakhanov of Moscow State University. "Our results reveal the mechanisms behind the growth of blood clots that are critical for the development of novel drugs and diagnostic assays."
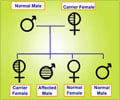
Blood clotting is crucial for preventing excessive blood loss when vessels are damaged. It relies on a network of proteins, including thrombin and factor XI, which are activated upon injury and result in the formation of fibrin—the protein that makes up clots. Patients with hemophilia C lack factor XI, and it has been a long-standing mystery why they experience uncontrollable bleeding even though they're missing only one component of the clotting network.
To answer this question, Ataullakhanov and his team developed an imaging method that allowed them to visualize the spread of fibrin clots by monitoring thrombin activity. After filling an experimental chamber with blood and triggering the clotting cascade, they made a novel observation: thrombin propagates through blood in steady waves from the activation site to distances farther away, similar to how electrical impulses travel through neurons.
These traveling waves were not apparent in blood from a patient with hemophilia C. Computer simulations revealed that factor XI is crucial for the spread of the waves far away from the activation site, a process that is necessary in order to seal large wounds. These results can explain why hemophilia C patients experience severe bleeding in response to large injuries or surgery, but not to minor wounds that do not require long-distance clotting.
Although traveling waves are important for normal blood clotting, they can also lead to complications related to blood-flow obstruction. Thus, the results have important clinical implications for not only hemophilia, but also stroke, sudden cardiac death, and other serious cardiovascular disorders.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert