In a pathbreaking study, researchers seem to have zeroed in on how skin cancer grows,which could pave the way for strategies to contain its spread.
In a pathbreaking study, researchers seem to have zeroed in on how skin cancer grows,which could pave the way for strategies to contain its spread.
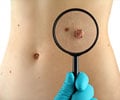
Although skin cancer is easily treated when caught early, it usually becomes fatal if it spreads to other parts of the body.Dr Lesley Walker, Cancer Research UK's director of information, says the findings will provide "new approaches for cancer therapy".
Scientists made the breakthrough in a study of people with a severe type of the skin-blistering disease called Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex.
It is known that people with that particular strain are more at risk of getting a skin cancer called basal cell carcinoma - but were not sure why.
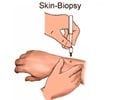
For the study, researchers at Cancer Research UK's cell structure group at the University of Dundee compared cells of people with EBS to those without.
When the EBS cells were damaged - or rubbed enough to cause blistering - their structure changed to stop them dying.
Advertisement
"Even slight damage to the skin of people with EBS can kick-start a signalling pathway which prevents the skin from killing and clearing damaged cells," the Daily Express quoted Dr David Russell, Cancer Research UK scientist and the study's lead author, as saying.
Advertisement
The study has been published in Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Source-ANI
SAV