Researchers at Henry Ford Hospital have found that a specific microRNA, released by the stem cells following a stroke, helps in better neurological recovery in animals.
The study, to be published in the journal Stem Cells, is available at ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23630198.
Although most stroke victims recover some ability to voluntarily use their hands and other body parts, nearly half are left with weakness on one side of their body, while a substantial number are permanently disabled.
Currently no treatment exists for improving or restoring this lost motor function in stroke patients, mainly because of mysteries about how the brain and nerves repair themselves.
"This study may have solved one of those mysteries by showing how certain stem cells play a role in the brain's ability to heal itself to differing degrees after stroke or other trauma," says study author Michael Chopp, Ph.D., scientific director of the Henry Ford Neuroscience Institute and vice chairman of the department of Neurology at Henry Ford Hospital.
The researchers noted that Henry Ford's Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee approved all the experimental procedures used in the new study.
Advertisement
The new study showed for the first time that a specific microRNA, miR-133b, carried by these exosomes contributes to functional recovery after a stroke.
Advertisement
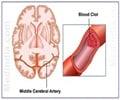
Stroke was induced under anesthesia by inserting a nylon thread up the carotid artery to occlude a major artery in the brain, the middle cerebral artery. MSCs were then injected 24 hours after the induction of stroke in these animals and neurological recovery was measured.
As a measure on neurological recovery, rats were given two types of behavioral tests to measure the normal function of their front legs and paws – a "foot-fault test," to see how well they could walk on an unevenly spaced grid; and an "adhesive removal test" to measure how long it took them to remove a piece of tape stuck to their front paws.
Researchers then separated the disabled rats into several groups and injected each group with a specific dosage of saline, MSCs and MSCs with increased or decreased miR-133b, respectively. The two behavioral tests were again given to the rats three, seven and 14 days after treatment.
The data demonstrated that the enriched miR-133b exosome package greatly promoted neurological recovery and enhanced axonal plasticity, an aspect of brain rewiring, and the diminished miR-133b exosome package failed to enhance neurological recovery
While the research team was careful to note that this was an animal study, its findings offer hope for new ways to address the single biggest concern of stroke victims as well as those with neural injury such as traumatic brain injury and spinal cord damage – regaining neurological function for a better quality of life.
Source-Eurekalert