Alzheimer's disease can now be detected early with a new technology developed called retinal hyperspectral imaging (rHSI). Currently, about 5.4 million are affected with AD in the U.S. and is estimated to rise to 16 million by 2050.

‘Alzheimer's disease can now be detected early with a new technology developed called retinal hyperspectral imaging (rHSI).’
Read More..




Damage to the brain from Alzheimer's disease occurs years before patients exhibit symptoms. Attempted therapies have been unsuccessful largely because there is no measurable indicator -- or biomarker -- for Alzheimer's disease before it is already symptomatic and advanced.Read More..
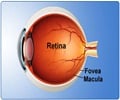
The eye's retina is considered the developmental extension of the brain and can be accessed non-invasively. In a recently published study in the ACS Chemical Neuroscience journal, University of Minnesota Professors Robert Vince and Swati More researched a promising retinal biomarker using a hyperspectral imaging technique for early Alzheimer's disease detection.
The hyperspectral imaging technique allows for the analysis of a wide spectrum of light outside of -- but not excluding -- primary colors that detect the biomarker of Alzheimer's disease.
The research team examined the potential of retinal hyperspectral imaging to detect biochemical changes present at the early stages of Alzheimer's disease. Specifically, the technique characterizes light scatter changes in the retina of Alzheimer's disease patients when compared with healthy participants.
The process, which has been used in preclinical trials and a human pilot study, scans a patient's eye to detect small quantities of a protein long before they collect in large enough clusters to form plaques in the brain -- a biological sign of Alzheimer's disease progression. The test is non-invasive and is conducted in less than 10 minutes.
Advertisement
An analysis of the retinal hyperspectral imaging (rHSI) data displayed that:
- The highest detectable light signal was obtained in the MCI cohort when compared to the advanced Alzheimer's disease participants;
- The signal suggests higher sensitivity of this technique toward early stages of the disease;
- The rHSI signature also correlated with memory scores in the MCI participants;
- The rHSI signature is unaffected by pre-existing eye conditions, such as mild to moderate cataracts or glaucoma, peripapillary atrophy, etc.
Advertisement
"In collaboration with our industry partner, RetiSpec, we hope to accelerate clinical development of this early detection technique and provide existing or new treatments the best chance for success," added Vince.
Source-Eurekalert