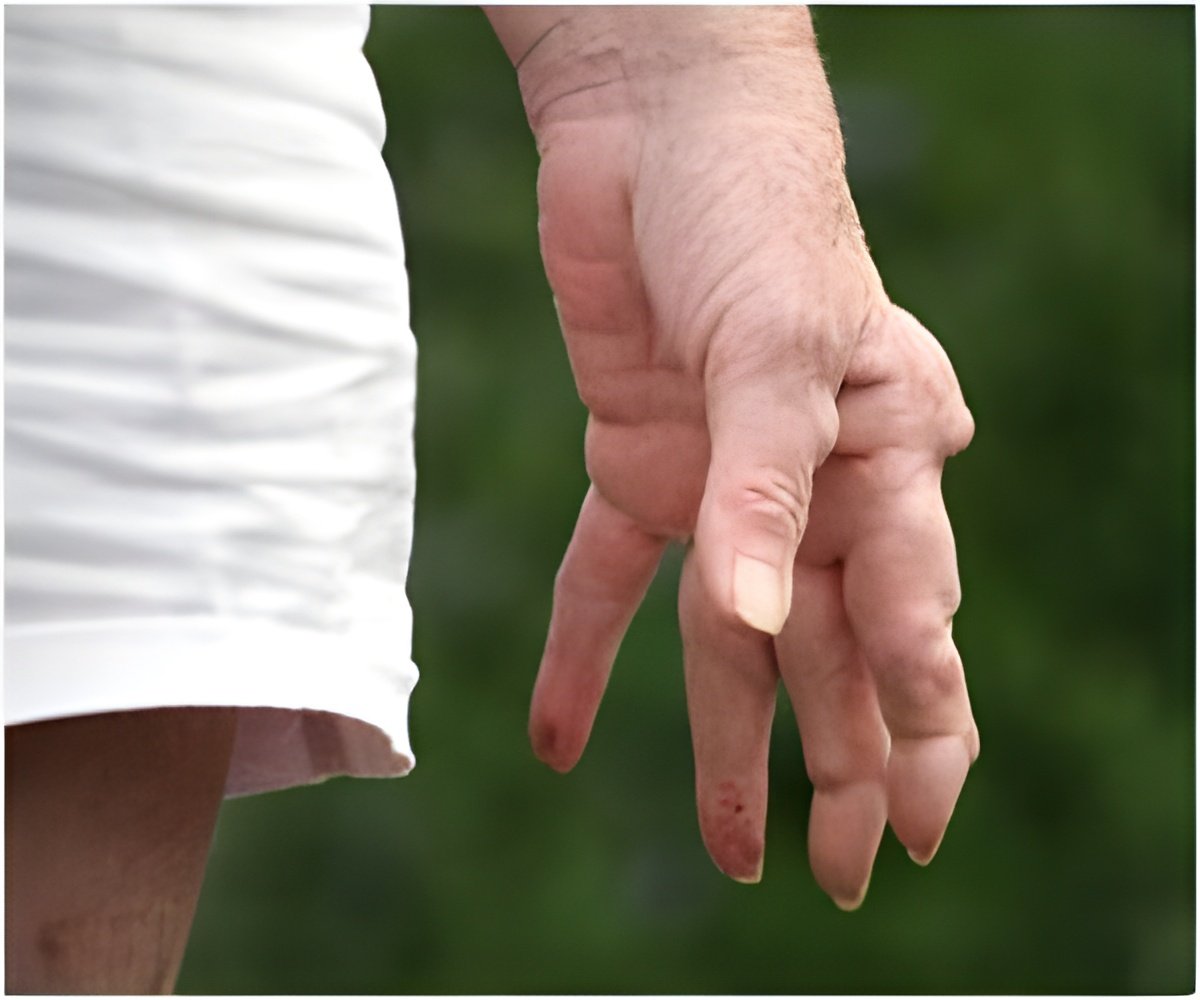
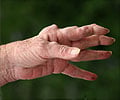
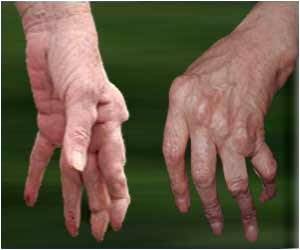
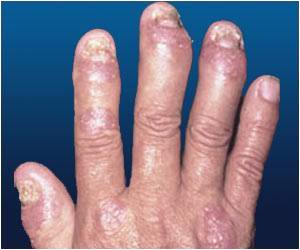
A new study suggests that low levels of testosterone in men may indicate the possibility of developing rheumatoid arthritis later in life.
In a recent study published online in the Annals of the Rheumatic Disease, researchers suggest that low levels of sex hormone, testosterone, in men may indicate a heightened risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis later in life.
Researchers from Lund University in Sweden identified men with rheumatoid arthritis from a large health survey called the, which tracked the health of more than 33,000 people from 1974. They were able to analyze the blood samples of 104 men who developed rheumatoid arthritis during later stages of life and compared it with the samples of 174 men of same age who did not develop the disease.
Investigators measured the various sex hormone levels in the blood samples and found that men who went on to develop the disease had low levels of testosterone many years before the occurrence of the inflammatory disease.
As the difference in testosterone levels was very small, the authors suggest that the findings need to be validated with other population groups.
Source-Medindia