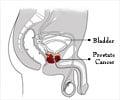
A natural form of sugar could offer a new, noninvasive way to precisely image tumors and potentially see whether cancer medication is effective.
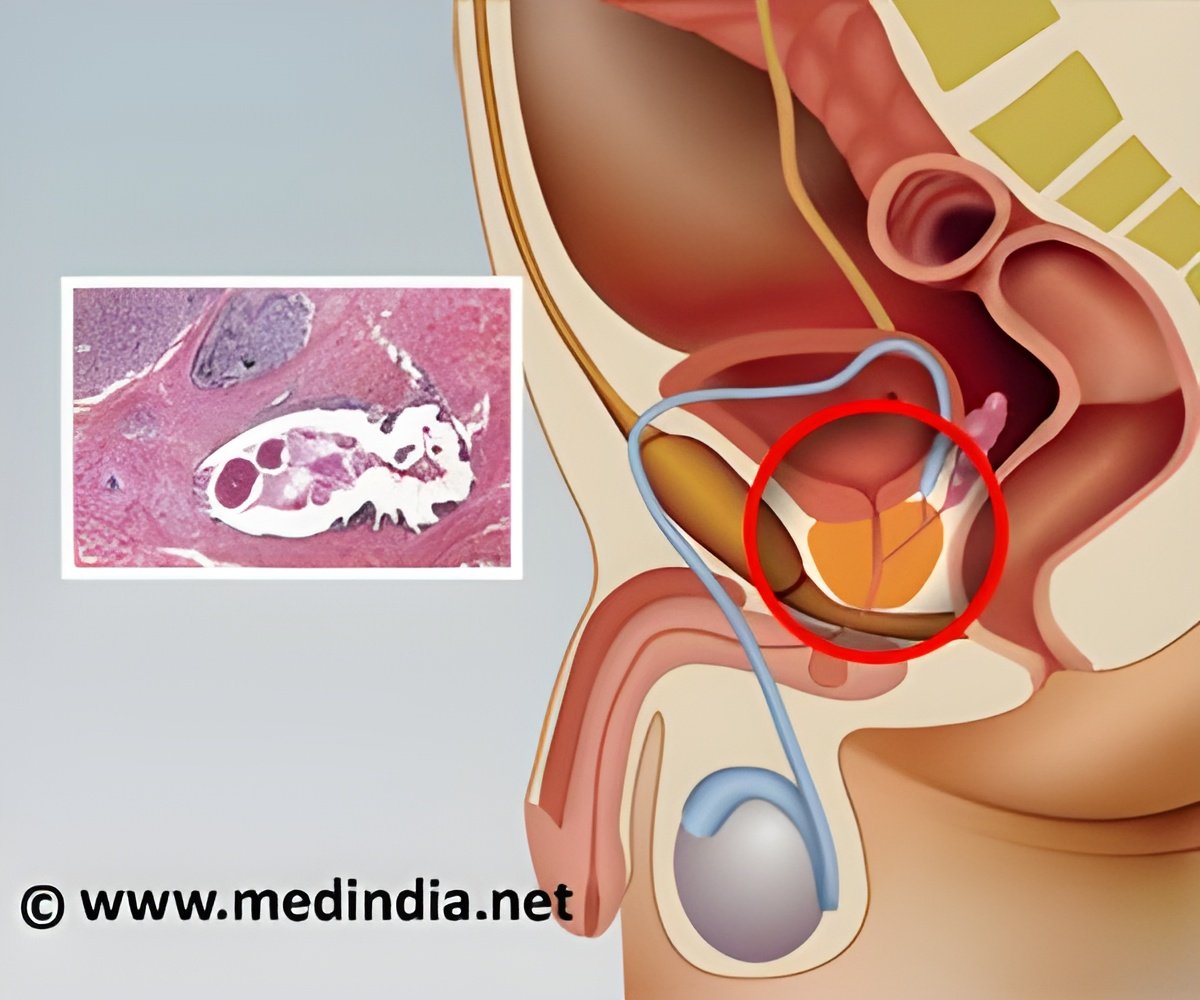
Now, a 31-patient study performed by scientists at UCSF and their collaborators at GE Healthcare has shown that the technology is safe in humans and effectively detects tumors in patients with prostate cancer. Findings appeared online in the Aug. 14, 2013, issue of Science Translational Medicine.
While this first-in-human study was designed to identify a safe dosage and verify effectiveness, it lays the groundwork for using the technology to diagnose a variety of cancers and track treatment noninvasively, without conducting repeated biopsies.
"We now have a safe dose for patients – that was our primary goal," said Sarah J. Nelson, PhD, a UCSF professor of radiology and director of the Surbeck Laboratory of Advanced Imaging at UCSF, who was lead author on the study and led a diverse team on this project.
"In animal models, the amount of lactate over pyruvate is directly related to the aggressiveness of the cancer. We also have a lot of data that show it's reduced in cancers after treatment," she said. "This is a very ubiquitous molecule that will be important in tailoring treatments to specific individuals."
Prostate cancer is the most common form of cancer, with more than 200,000 new cases reported each year in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The increased use of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels for screening men has been widely recognized as having identified more patients with prostate cancer at an earlier, and potentially more treatable, stage. Many of those tumors are slow growing, but it is difficult to predict which those are.
Advertisement
"There are natural risks in any treatment for prostate cancer, including radiation therapy and surgery. Those risks can have an enormous impact on the patient's quality of life," said UCSF oncologist Eric Small, MD, a co-author on the paper, UCSF professor of medicine and urology, and deputy director of the UCSF Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center. "This technology begins to give us the ability to more accurately assess the extent and risk of an individual patient's actual cancer, which is absolutely critical, but so far is largely an unmet medical need."
Advertisement
UCSF pulled together a team of researchers ranging from oncologists and radiologists to clinical pharmacists with the precise knowledge of building clean-rooms for pharmaceutical production. At the time, Nelson also was the scientific director of the UCSF arm of the California Institute for Quantitative Biosciences (QB3), which supports both basic and translational science at the crossroads of biology and the quantitative sciences, such as imaging and bioinformatics.
"UCSF and QB3 offered an unusual combination of talent all in one location. They brought together the best engineering from UC Berkeley and the best bioscience and pharmacy knowledge from UCSF, and are now demonstrating the technology in a world-renowned academic medical center," said Jonathan Murray, managing director of Research Circle Technology at GE Healthcare and a co-author on the paper. "At GE Healthcare, we are delighted with the speed of progress of this collaboration. The science is very exciting."
In the clinical research study, which started in December 2010, the researchers labeled pyruvate with carbon-13 and injected this "hyperpolarized pyruvate" imaging agent into 31 prostate cancer patients in the UCSF Medical Center and UCSF Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center. The team then used an MRI to follow pyruvate and its conversion to lactate in the prostate. As in previous studies in mice, the higher, more intense signals indicated a more rapid conversion to lactate, possibly a sign of more aggressive cancer. In contrast, there was very limited conversion detected in normal prostate.
The study deliberately focused on patients with low-grade tumors who had not yet received treatment, to identify the safe and appropriate dosage of pyruvate needed. Future studies will use the technology to assess the effectiveness of a patient's cancer therapy in shrinking their tumor – knowledge that will enable physicians to assess the dosage of chemotherapy needed on an individual basis.
While potential commercial use is still five to 10 years away, the UCSF team has received grants to extend the technology for studies in patients with cancers of the brain, breast, liver, lymph glands, pancreas and prostate. GE Healthcare also has developed equipment to process the hyperpolarized pyruvate in a less technical environment, enabling a broader clinical trial in the future.
Source-Eurekalert





![Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA] Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA]](https://www.medindia.net/images/common/patientinfo/120_100/prostate-specific-antigen.jpg)