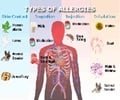
Scientists across Europe are working towards developing a treatment for one of the most common and dangerous conditions for humans - food allergy.
Scientists across Europe are working towards developing a treatment for one of the most common and dangerous conditions for humans - food allergy.
The initiative called the Food Allergy Specific Therapy (FAST) research project has Dr Clare Mills of the Institute of Food Research as a lead partner."All people with food allergy can do is avoid the foods to which they are allergic. The threat of severe anaphylaxis has a great impact on their quality of life," he said.
Attempted treatment with allergen-specific immunotherapy, where a patient received monthly injections with an allergen extract for three to five years, failed because it could cause anaphylaxis as a side effect.
Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction involving the whole body, often within minutes of exposure to the allergen.
Peanut allergy is the most widely known cause, but other causes of anaphylaxis include other foods, insect stings, latex and drugs. If untreated in time it can be fatal.
In the FAST project, scientists will use modified variants of allergic proteins that are hypoallergenic and therefore safer. The proteins will be purified making them more effective and making it easier to control the dose.
Advertisement
Allergies to fish and fruit are among the most common in Europe. In fish allergy the protein responsible is parvalbumin and in fruit it is lipid transfer protein (LTP). Modified hypo-allergenic versions of these proteins will be produced at tested as potential treatments.
Advertisement
He added: "The risk of unintentional exposure due to cross-contamination of foods, or while eating in restaurants or at parties, will decrease. This will take away lot of the anxiety that has a negative impact on the quality of life of food allergy sufferers."
Source-ANI
LIN