A research on the experimental cancer drug that is capable of passing through the blood -brain barrier was studied.
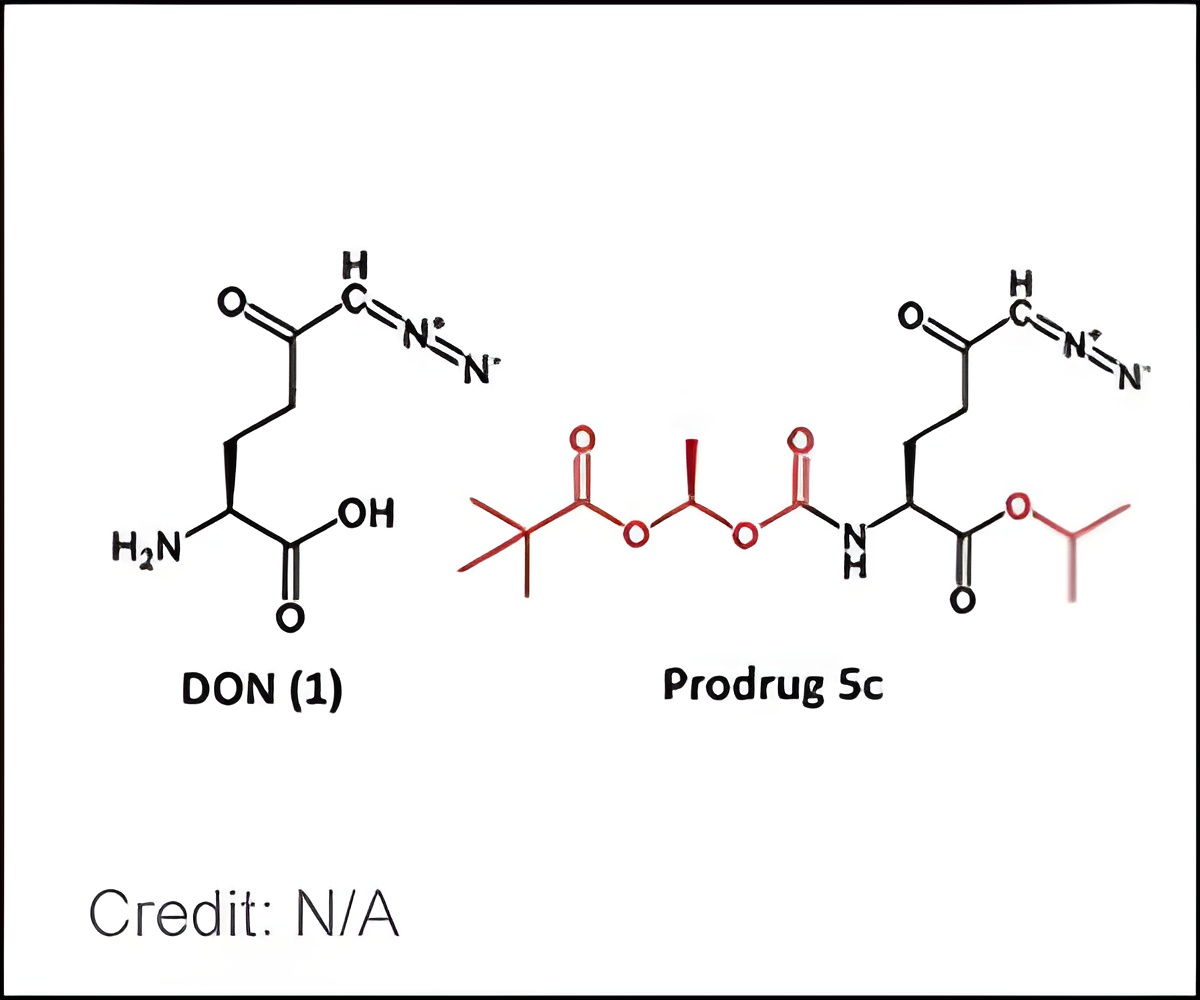
"We wondered whether we could make a safer and more tolerable form of DON by enhancing its brain penetration and limiting its exposure to the rest of the body and, thus, toxicity," says Barbara Slusher, Ph.D., professor of neurology, medicine, psychiatry, neuroscience and oncology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and director of Johns Hopkins Drug Discovery.
Slusher teamed up with Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center immunologist Jonathan Powell, M.D., Ph.D., who has studied how cancer cells use different metabolic pathways to evade destruction by immune cells.
"A tumor uses aggressive metabolism to grow, sucking up all the surrounding nutrients, which leads to a very oxygen-poor, acidic environment that is not conducive to cancer-killing immune cells," says Powell, who is an associate director of the Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy.
Powell suspects that using glutamine-blocking drugs to target tumor metabolism could make the environment around a tumor less harsh, slow down its growth and give the immune system a chance to attack the cancer cells. "The hope is to enhance certain immunotherapy drugs by adding such glutamine antagonists," says Powell.
To alter DON, Slusher and her drug discovery team designed and synthesized various derivatives, focused on making the drug more lipid soluble, or lipophillic, a trait known to aid passage through the blood-brain barrier. Once inside the brain, the new derivatives are designed to rapidly metabolize back to DON.
Advertisement
"We showed that we can modify these drugs to have further specificity to target the brain and limit toxicity to the rest of the body," says Slusher. "This strategy can potentially be used to develop tailored drugs for different cancers."
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert