Scientists from Iowa State University have discovered an enzyme that makes tuberculosis resistant to a human body's natural defense.
Scientists from Iowa State University have discovered an enzyme that makes tuberculosis resistant to a human body's natural defense.
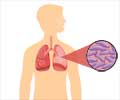
When most infections are introduced into humans, the body defends itself with certain cells - called macrophage cells - that kill the invading microorganisms.The macrophage cells engulf and destroy these microbes, such as the Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Lead researcher Reuben Peters, associate professor in the department of biochemistry, biophysics and molecular biology has found that TB bacteria produces a defensive molecule that prevents the macrophage cells from destroying them.
He and his team have named the defensive molecule edaxadiene.
Without edaxadiene, tuberculosis cells would have a reduced ability to resist being killed by the macrophage cells.
"We have inhibitors that bind tightly to one of the enzymes that make edaxadiene in a test tube," said Peters.
Advertisement
"Their genetic sequences are more than 99.9 percent identical," said Peters. "However, whereas, tuberculosis causes disease in humans, the bovis variety is much less infectious in humans, although it does cause disease in cattle."
"By exploring ways to block the production of this molecule, Dr. Peters is pioneering a new approach for combating this deadly pathogen," he added.
The study appears in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Source-ANI
ARU