The hormone leptin, which is critical for normal food intake and metabolism, appears to regulate bone mass and suppress appetite, according to Yale researchers.
The hormone leptin, which is critical for normal food intake and metabolism, appears to regulate bone mass and suppress appetite, according to Yale researchers.
The hormone appears to regulate bone mass and weight by acting mainly through serotonin pathways in the brain."Our study challenges the view that the hypothalamus is the critical brain site where leptin acts directly to alter neuronal circuit function to suppress appetite and bone metabolism," said Yale researcher and study co-author Tamas Horvath.
"We've now found a novel explanation for how leptin can act on the brain," Horvath added.
Food intake is influenced by signals that travel from the body to the brain. Leptin is one of the molecules that signal the brain to modulate food intake.
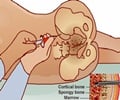
It is produced in fat cells and informs the brain of the metabolic state. If animals are missing leptin, or the leptin receptor, they eat too much and become severely obese.
To determine whether leptin regulates bone mass through serotonin pathways, Horvath and his colleagues analyzed multiple lines of mice that were genetically altered to remove serotonin in the brain.
Advertisement
"When the pathway is turned on, the mice ate more, gained weight and had more bone mass. This might be why obese people tend to have much lower incidences of osteoporosis," the expert added.
Advertisement
Source-ANI
RAS