Scientists in France and America have recommended that the World Health Organization (WHO) must review, and adjust its guidelines for the fight against tuberculosis (TB).
Scientists in France and America have recommended that the World Health Organization (WHO) must review, and adjust its guidelines for the fight against tuberculosis (TB).
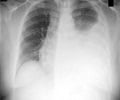
TB is a global threat that affects more than 10 million people each year.Dr. Dick Menzies, of the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Center(RI-MUHC), closely studied current tuberculosis treatment guidelines and urged for an urgent review.
"Our first study is a systematic review and meta-analysis of 57 studies, involving more than 20,000 patients from around the world. It demonstrates that the treatment period should be extended for people affected by the active form of tuberculosis for the first time. Specifically, the study recommends that these patients should be treated with Rifampin for six months, instead of two months; the additional four months will help maximize the medication's effectiveness," said Menzies.
In another study, the researchers assessed guidelines for patients who have been treated but not cured.
"Currently, these patients receive a cocktail of drugs over the course of eight months, which can result in drug resistance and a failure to cure in up to 45 per cent of cases. More studies are needed to determine the optimal strategy. However, we believe that it is essential - indeed, of critical importance - to thoroughly review these guidelines," said Menzies.
"Our challenge as researchers is to put into place the most effective strategies for the treatment of tuberculosis, to determine the optimal length for courses of treatment so as to avoid relapse, and to formulate more effective combinations of drugs in order to avoid drug resistance," he added.
Advertisement
The studies have been published in two separate articles in the journal PLoS Medicine.
Advertisement
ARU