Sexually active gay men are at a very high-risk of acquiring a new, highly antibiotic-resistant strain of the MRSA bacteria .
Sexually active gay men are at a very high-risk of acquiring a new, highly antibiotic-resistant strain of the so-called MRSA bacteria widely know as the ‘superbug’, reveals a new study.
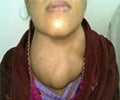
MRSA stands for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.The bacteria appear to be transmitted most easily through intimate sexual contact, but can spread through casual skin-to-skin contact or contact with contaminated surfaces.
"These multi-drug resistant infections often affect gay men at body sites in which skin-to-skin contact occurs during sexual activities," said Binh Diep, PhD, UCSF postdoctoral scientist at San Francisco General Hospital Medical Centre and lead author of a report on the finding.
"But because the bacteria can be spread by more casual contact, we are also very concerned about a potential spread of this strain into the general population,” Diep added.
The researcher said that a good scrubbing with soap and water might be the most effective way to prevent skin-to-skin contact transmission, especially after sexual activities.
The study is based on review of medical records from outpatient clinics in San Francisco and Boston as well as nine of 10 medical centres serving San Francisco.
In a second part of the study based on patient medical charts, the scientists found that sexually active gay men in San Francisco are about 13 times more likely to be infected than the general population.
"The potential widespread dissemination of multi-resistant form of USA300 into the general population is alarming," Diep said.
The microbe is known as "multidrug-resistant, community-associated MRSA USA300."
The scientists conclude that research should be undertaken to explore the link between MRSA and unsafe sexual risk behaviours.
The study is published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Source-ANI
ANN/C