A new study has discovered six major factors that can affect a woman's happiness with the outcome of her breast surgery.
A new study has discovered six major factors that can affect a woman's happiness with the outcome of her breast surgery.
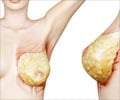
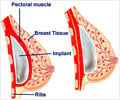
The research led by Andrea Pusic, from Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, has determined that, as well as final breast appearance, there are five other major concerns that influence surgical satisfaction.The researchers interviewed 48 women who had undergone breast reduction, augmentation or reconstruction, and discovered that their main concern was how they looked.
"Patient satisfaction with breast appearance was without doubt the key theme and is a salient factor in determining the success of breast surgery. However, other themes were also identified that related to the broadened notion of quality of life, including concepts such as physical, psychological and sexual well-being," Pusic said.
The six main areas that affect how happy they are with the surgery are, satisfaction with breasts; satisfaction with overall outcome; psychosocial well-being; sexual well-being; physical well-being; and satisfaction with the process of care.
Although these six themes were common to women in all three groups, the importance ascribed to each was seen to vary by surgical group.
"While physical well-being was of only limited importance to breast augmentation patients (only a few reported pain and discomfort post-operatively), it was often the main motivation behind breast reduction surgery (patients reported substantial pain and activity limitations pre-operatively), and was often an issue for women following breast reconstruction," she said.
Advertisement
The authors hope that their findings may be used to guide the development of patient education materials and facilitate shared medical decision-making.
Advertisement
Source-ANI
LIN