Deep learning and synthetic data unite to predict better outcomes in atrial fibrillation ablation.
The Efficacy of Artificial Intelligence in the Detection and Management of Atrial Fibrillation
Go to source).
‘Training on synthetic fibrosis images achieved a 0.943 ROC-AUC—nearly matching real MRI data (0.952). AI is transforming heart treatment.#aiinhealthcare #medindia
’





Advertisement
Challenge of Predicting AF Ablation Outcomes
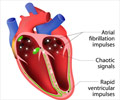
Atrial fibrillation (AF) remains the most common heart rhythm disorder, and its treatment through ablation is often hit-or-miss due to patient-specific variations in cardiac fibrosis.Existing methods like LGE-MRI provide valuable insights but lack scalability and diversity. With limited patient data, deep learning models struggle to generalize outcomes effectively. This challenge opens the door to synthetic solutions that can mimic real-world variability without the constraints of clinical data availability.
Advertisement
Generating Synthetic Fibrosis with Diffusion Models
To fill the data gap, researchers used denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs) to generate lifelike synthetic fibrosis distributions. Trained on 100 real LGE-MRI scans, the model produced high-qualityAdvertisement
Training the Deep Learning Pipeline for AF Predictions
These synthetic fibrosis maps were integrated into 3D digital twin heart models for AF simulations, both pre- and post-ablation. The deep learning pipeline, trained on this enhanced dataset, delivered outstanding predictive accuracy—nearly matching the performance of models trained on real patient data (ROC-AUC 0.943 vs. 0.952). This breakthrough not only reduces dependence on clinical scans but also accelerates the development of personalized, AI-powered AF treatment strategies.Reference:
- The Efficacy of Artificial Intelligence in the Detection and Management of Atrial Fibrillation - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39925585/#)