Californian scientists have identified a potential new target to reduce stroke damage in patients.
The researchers, from the University of California in Los Angeles, said that doing this in mice helped reverse the effects of a stroke, reports the BBC.
A treatment based on this approach could be given days later, while conventional treatments need far quicker action.
The Stroke Association said far more testing would be needed on any new drug.
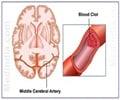
Strokes happen when an area of brain cells is starved of oxygen, due to a blocked or burst blood vessel.
Cells start to die in the affected area, and while nothing can bring these back, scientists know the cells immediately surrounding the damaged area play a crucial role in the ability of the brain to recover and compensate for the damage.
Advertisement
The researchers found that a natural process within the surrounding brain cells appeared to be getting in the way of recovery.
When strokes were induced in mice, giving them a drug, which blocked the effects of this molecule, appeared to improve their ability to recover movement.
Altering the genetic make-up of the mice to be less responsive to GABA produced similar results, adding weight to the theory.
The researchers believe that their work offers the prospect of a new type of drug to boost recovery in stroke patients.
The study appears in the journal Nature.
Source-ANI