Hypersensitivity experienced by chronic pain patients may result from hyperactive brain networks.
‘Linking up different centers in the brain after a stimulus is normally a gradual process, but chronic pain patients have conditions that predispose them to linking up in an abrupt, explosive manner.’





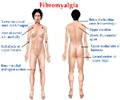
Research teams from the University of Michigan and Pohang University of Science and Technology in South Korea report evidence of ES in the brains of people with fibromyalgia, a condition characterized by widespread, chronic pain. "For the first time, this research shows that the hypersensitivity experienced by chronic pain patients may result from hypersensitive brain networks," says co-senior author Richard Harris, Ph.D., associate professor of anesthesiology at Michigan Medicine with the Chronic Pain and Fatigue Research Center. "The subjects had conditions similar to other networks that undergo explosive synchronization."
In ES, a small stimulus can lead to a dramatic synchronized reaction in the network, as can happen with a power grid failure (that rapidly turns things off) or a seizure (that rapidly turns things on). This phenomenon was, until recently, studied in physics rather than medicine. Researchers say it's a promising avenue to explore in the continued quest to determine how a person develops fibromyalgia.
"As opposed to the normal process of gradually linking up different centers in the brain after a stimulus, chronic pain patients have conditions that predispose them to linking up in an abrupt, explosive manner," says first author UnCheol Lee, Ph.D., a physicist and assistant professor of anesthesiology at Michigan Medicine. These conditions are similar to other networks that undergo ES, including power grids, Lee says.
'Electrically unstable' findings
Advertisement
Lee's research team and collaborators in South Korea then used computer models of brain activity to compare stimulus responses of fibromyalgia patients to the normal condition. As expected, the fibromyalgia model was more sensitive to electrical stimulation than the model without ES characteristics, Harris says.
Advertisement
He says this type of modeling could help guide future treatments for fibromyalgia. Since ES can be modeled essentially outside of the brain or in a computer, researchers can exhaustively test for influential regions that transform a hypersensitive network into a more stable one. These regions could then be targeted in living humans using noninvasive brain modulation therapies.
George Mashour, M.D., Ph.D., co-senior author and professor of anesthesiology at Michigan Medicine, says, "This study represents an exciting collaboration of physicists, neuroscientists and anesthesiologists. The network-based approach, which can combine individual patient brain data and computer simulation, heralds the possibility of a personalized approach to chronic pain treatment."
Source-Eurekalert