How genes coordinate the complex process of eye formation and how a rare pediatric eye cancer progresses.
A genetic discovery led by scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital helps answer a long-standing mystery about the eyes of vertebrates, and may translate into a deeper understanding of how genes coordinate the complex process of eye formation and how a rare pediatric eye cancer progresses.
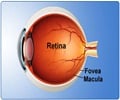
“A series of complex developmental processes must be carefully orchestrated for the eye to form correctly,” said Michael Dyer, Ph.D., associate member in the St. Jude Department of Developmental Neurobiology. “One important aspect of this coordination is that retinal thickness be the same, irrespective of eye size. For example, the mouse eye is about 5,000 times smaller than that of the elephant eye, but the retinal thickness in these two species is comparable.”Working with mice, the researchers found that a gene called N-myc coordinates the growth of the retina and other eye structures to ensure the retina has the proper thickness necessary to convert light from the lens into nerve impulses that the brain transforms into images. Until their study, reported in the Jan. 15 issue of Genes & Development, almost nothing was known about the molecular mechanisms responsible for properly sizing the retina. Dyer is the paper’s senior author.
“This represents the first example of a role for a Myc gene in retinal development,” Dyer said. “On the basis of our data, we propose that N-myc plays a central role in coordinating retinal proliferation with eye growth during development.”
Genes in the Myc family carry out vital roles during prenatal development by regulating the proliferation, size, differentiation and survival of cells. Myc genes are also proto-oncogenes—genes in which a mutation enables them to transform normal cells into cancerous ones. Malfunctioning N-myc genes are often associated with pediatric neural cancers, including neuroblastoma, medulloblastoma and retinoblastoma.
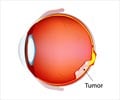
Recently, Dyer and his team identified the specific type of cell that gives rise to retinoblastoma, a potentially fatal malignant tumor in the retina that affects about 300 children in the United States annually. “The determination of N-myc target genes during retinal development may also contribute to the current understanding of retinoblastoma progression,” he said.
In the course of their study, the researchers discovered that N-myc is not involved in regulating cell survival or neuronal differentiation in the developing retina. However, the gene is crucial for the proper proliferation of retinal cells. In mice in which the scientists inactivated N-myc, the volume of the retina was significantly smaller than in mice with normally functioning N-myc.
Advertisement
The researchers hypothesize that N-myc’s activity occurs early in the cascade of reactions that control development of the retina and other eye components. Therefore, when something inactivates the gene, the result is both a reduction in retinal progenitor cell proliferation and a reduction in the signaling cues that coordinate the growth of the eye and retina.
Advertisement
Source-Newswise
LIN/V