Researchers at the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland, Dublin, have found that high blood pressure and high cholesterol may be associated with an increased risk of retinal vein occlusion,
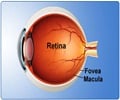
Researchers at the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland, Dublin, have found that high blood pressure and high cholesterol may be associated with an increased risk of retinal vein occlusion, a condition that causes vision loss.
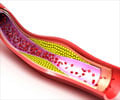
The team found that high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels appear to be risk factors for retinal vein occlusion.Retinal vein occlusion occurs when one or more veins carrying blood from the eye to the heart become blocked, according to background information in the article. Bleeding (hemorrhage) or fluid buildup (edema) may follow, damaging vision.
Paul R.A. O'Mahoney and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis of 21 previously published studies involving 2,916 individuals with retinal vein occlusion and 28,646 control participants without the condition.
The researchers pooled data from all the studies and estimated the population-attributable risk, or the percentage of cases of retinal vein occlusion that could be attributed to hypertension (high blood pressure), diabetes and hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol).
Of patients with retinal vein occlusion, 63.6 percent had hypertension, compared with 36.2 percent of controls; those with high blood pressure had more than 3.5 times the odds of having retinal vein occlusion.
High cholesterol levels were more than twice as common among patients with retinal vein occlusion as those without (35.1 percent vs. 16.7 percent), and those with high cholesterol levels had an approximately 2.5-fold higher risk of retinal vein occlusion. Diabetes was slightly more prevalent among those with retinal vein occlusion than among those without (14.6 percent vs. 11.1 percent).
Advertisement
"Accordingly, we recommend that an assessment of blood pressure and both fasting lipid and glucose levels be routinely performed in adults with any form of retinal vein occlusion.
Advertisement
The study appears in the May issue of Archives of Ophthalmology, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
Source-ANI
SRM