Earlier sunscreens are thought to be toxic to the skin. The recent research has proved that the nano particles present in sunscreens do not penetrate and causes no toxicity after repeated application.
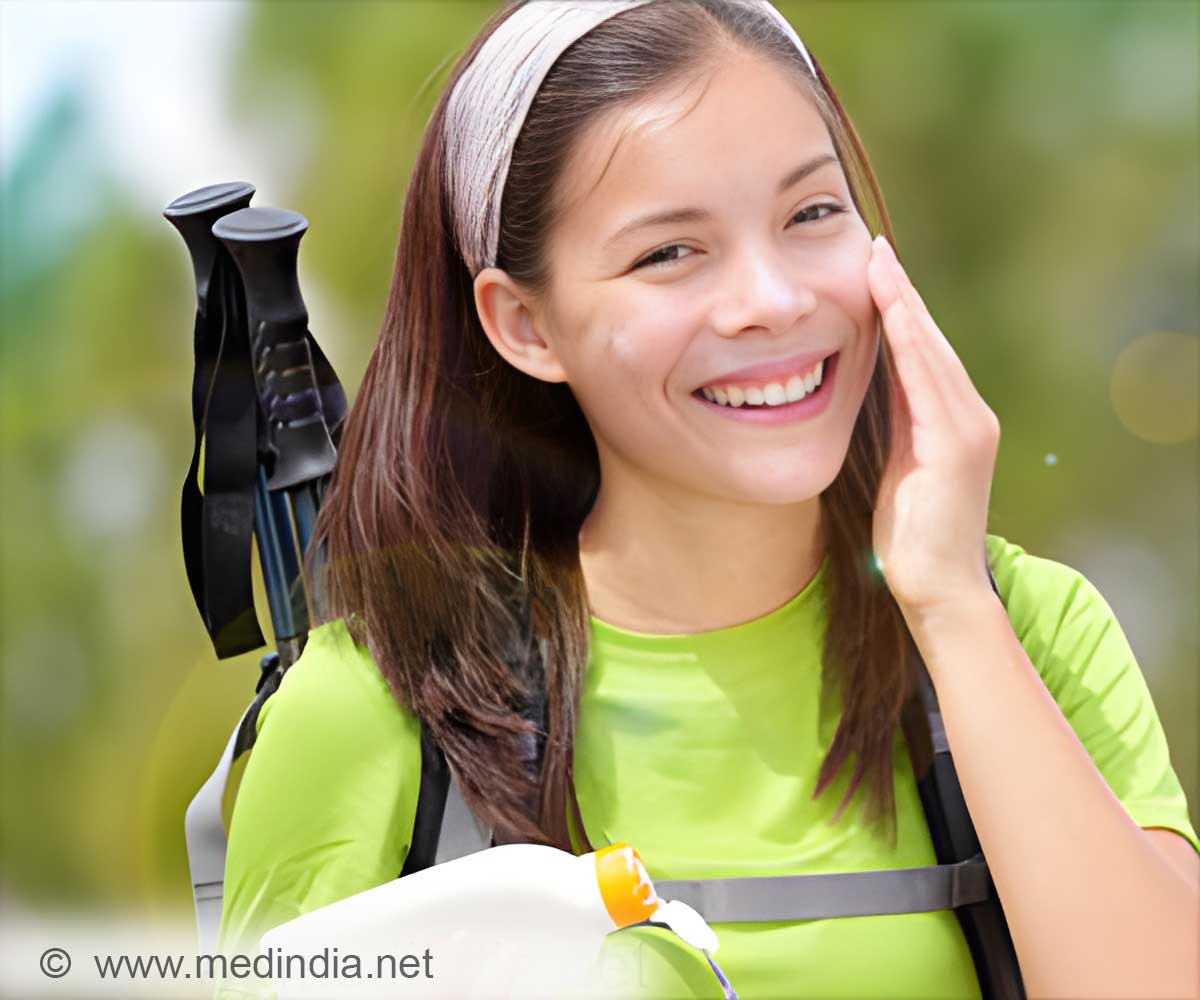

‘The nano particles used in the sunscreens neither penetrate the skin nor causes toxicity after repeated application and can prevent the damaging effects caused by prolonged exposure to sun.’





The research, published this week in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, refutes widespread claims among some public advocacy groups - and a growing belief among consumers - about the safety of nano particulate-based sunscreens. UQ and UniSA lead investigator, Professor Michael Roberts, says the myth about sunscreen toxicity took hold after previous animal studies found much higher skin absorption of zinc-containing sunscreens than in human studies.
"There were concerns that these zinc oxide nano particles could be absorbed into the epidermis, with toxic consequences, including DNA damage," Professor Roberts says.
The toxicity link was picked up by consumers, sparking fears that Australians could reduce their sunscreen use, echoed by a Cancer Council 2017 National Sun Protection Survey showing a drop in the number of people who believed it was safe to use sunscreens every day.
Professor Roberts and his co-researchers in Brisbane, Adelaide, Perth and Germany studied the safety of repeated applications of zinc oxide nano particles applied to five volunteers aged 20-30 years.
Advertisement
"We hope that these findings help improve consumer confidence in these products and in turn lead to better sun protection. The terrible consequences of skin cancer and skin damage caused by prolonged sun exposure are much greater than any toxicity posed by approved sunscreens."
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert