Can't exercise? Simply resort to hot water treatment as a new study finds that taking a hot bath can improve your inflammation, blood sugar levels.
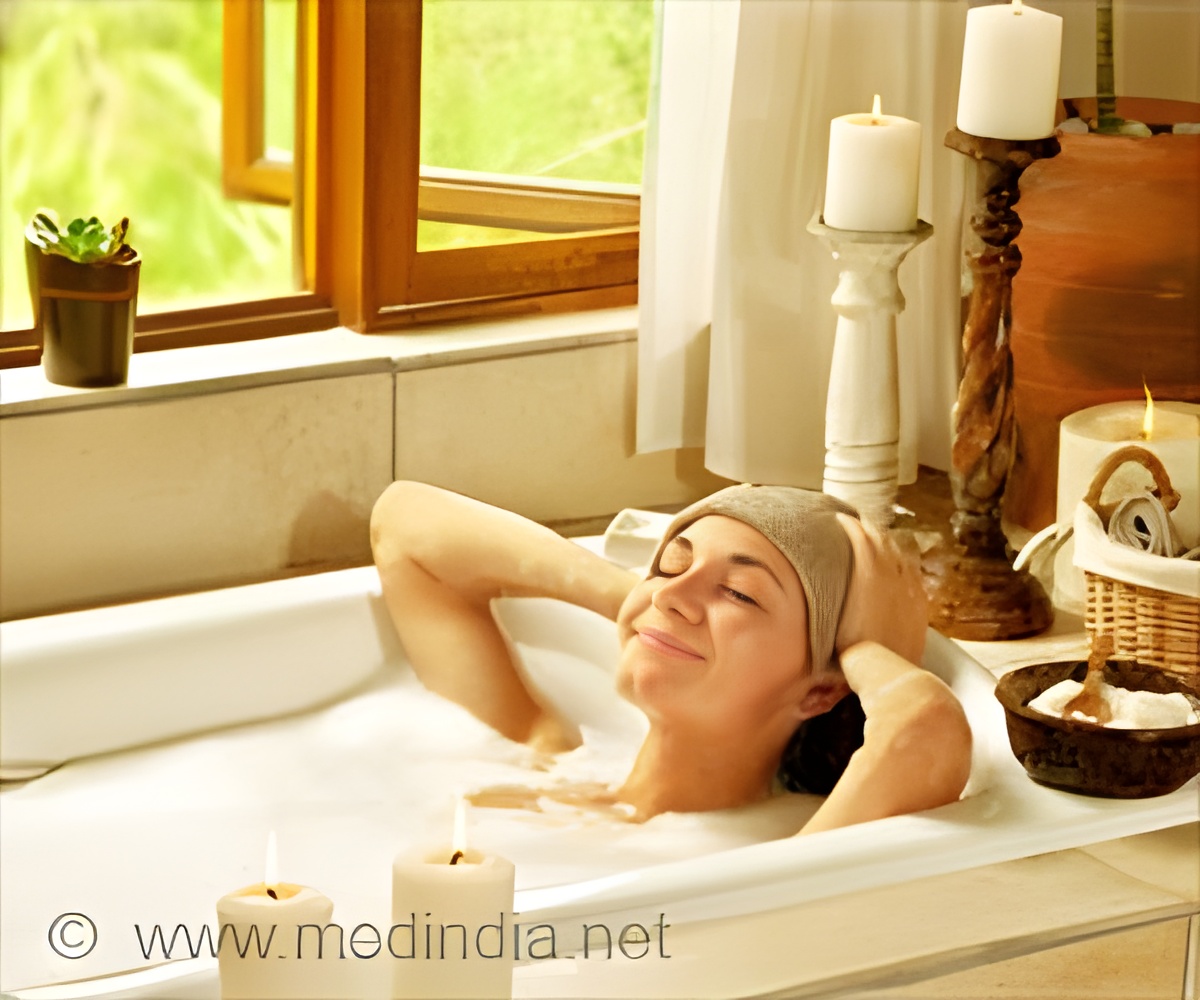

‘Can't exercise? Just resort to hot water treatment as a new study finds that taking a hot bath not only provides mental relaxation but also improve inflammation and metabolism in people who are unable to exercise.’
Read More..




Physical stress such as exercise can increase the level of an inflammatory chemical (IL-6), which activates the release of anti-inflammatory substances to combat unhealthily high levels of inflammation, known as chronic low-grade inflammation. Read More..
However, a hot-water immersion may "improve aspects of the inflammatory profile and enhance glucose metabolism in sedentary, overweight males and might have implications for improving metabolic health in populations unable to meet the current physical activity recommendations," said researchers including Christof Andreas Leicht from the Loughborough University in the UK.
For the study, the team included a group of sedentary, overweight men who participated in both hot-water immersion and ambient room temperature (control) trials separated by at least three days.
In the hot water trial, the volunteers sat immersed up to their necks in 102-degree Fahrenheit water.
The research team measured the men's heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature every 15 minutes throughout both the control and immersion conditions. Blood samples were taken again two hours after each session.
Advertisement
However, a two-week treatment period in which the men participated in daily hot-water baths showed a reduction of fasting blood sugar and insulin levels as well as improved low-grade inflammation at rest.
Advertisement