It is a fad these days to sport tattoos. Kids often show off their sticker tattoos. But adults go a step further. Permanent tattoos, which are
It is a fad these days to sport tattoos. Kids often show off their sticker tattoos. But adults go a step further. Permanent tattoos, which are permanent reminders throughout life, in different designs and shapes, are very popular. However there is a darker side to the whole affair. The study in the United States of America says that tattoos significantly increase the risk of hepatitis C infection.
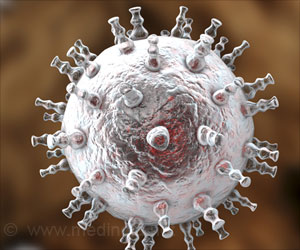
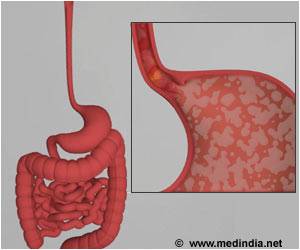
Hepatitis C is a viral infection of the liver, which can cause liver damage and may lead on to fatal liver disease. It is considered a major public health risk because it is a silent disease but can kill millions.Although there is no cure, antiviral drugs combined with interferon therapy can be useful. The treatment is very long and can extend upto a year. Unpleasant side effects include nausea, vomiting, headache, fatigue and depression.
Hepatitis C is spread by blood-to-blood contamination, says lead study author Robert Haley, MD, Chief of Epidemiology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Centre (UTSW) in Dallas. Injection drug abusers have an increased risk for hepatitis C because they often share needles. Healthcare workers, especially nurses, are also considered high risk for hepatitis C because of “accidental needle sticks”, he says.
It is in this context that tattoos assume significance. Tattoos also spread infection like needle stick injuries. Moreover this can also dangerously expose a person to accidental HIV infection. So people who have liking for tattoos have to be very careful to avoid these infections.
The best remedy would be to avoid reuse of tattoo needles. If many people are found using the same needle it is advisable to avoid tattooing itself. After all a healthy body without a tattoo is preferable over a very attractive tattooed body with hepatitis C.