High risk of acute kidney injury is estimated in patients undergoing treatment for infected total knee replacement.
‘High risk of acute kidney injury is estimated in patients undergoing treatment for infected total knee replacement. This emphasizes the importance of screening to identify patients with possible decreases in kidney function before two-stage exchange arthroplasty. Also, the risk of AKI related to pre-existing CKD and toxicity from ALBC spacers and IV antibiotics is highlighted.’





In the two-stage exchange arthroplasty, the knee implant is removed to enable treatment of the infection followed by placement of antibiotic-loaded bone cement (ALBC) spacers. The spacers deliver high doses of antibiotics directly and continuously to the site of the infection. Upon the eradication of the infection, another operation is performed to place new knee prosthesis. But the high doses of antibiotics from the spacers, in addition to IV antibiotics, may result in a toxic effect on the kidneys that contribute to AKI.
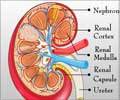
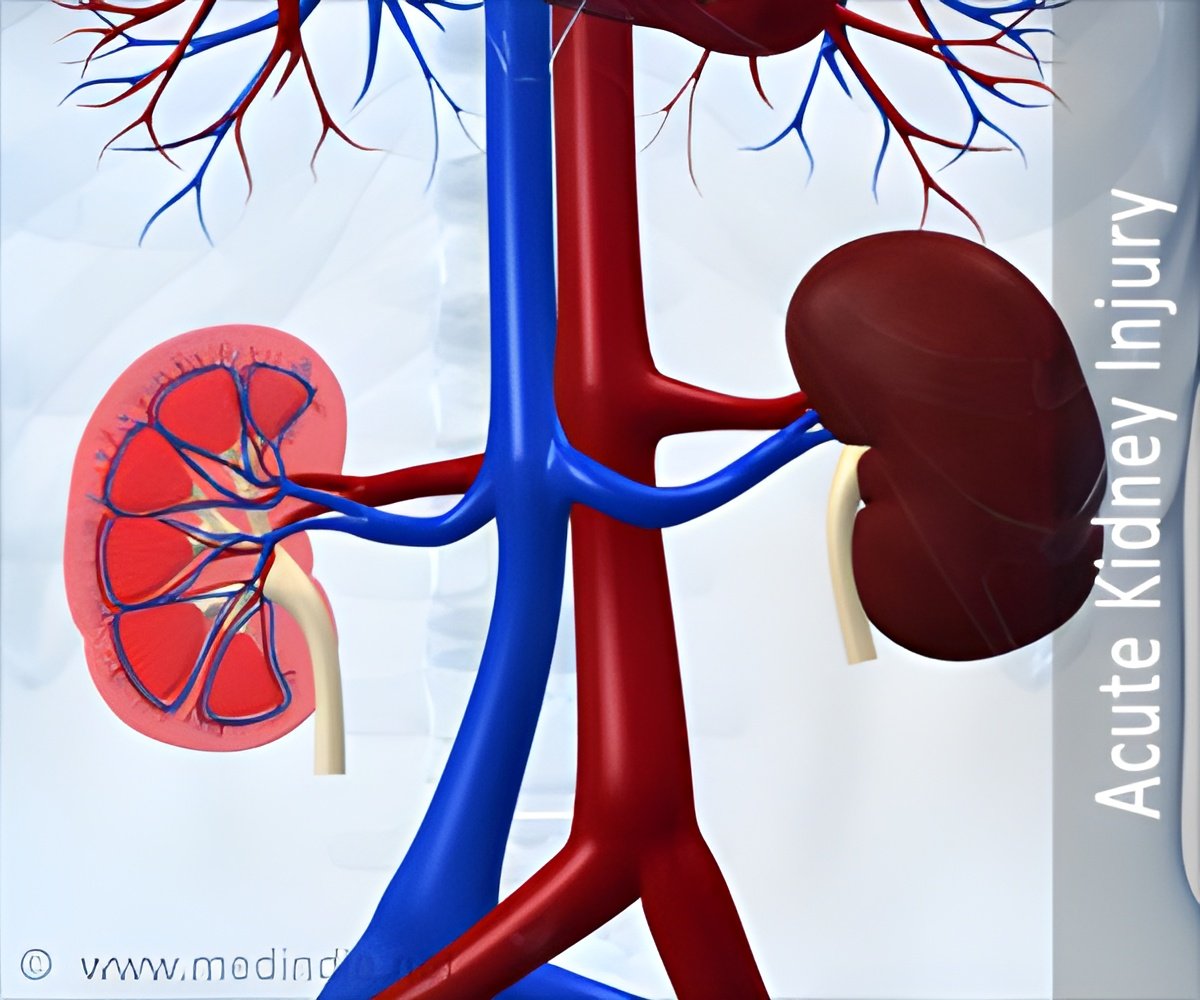
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a serious complication marked by a sudden decline in kidney function. There is only a little evidence about the risk of AKI related to ALBC spacers, IV antibiotics, and long-term outcomes of patients who develop AKI.
Acute kidney injury (AKI) with Arthroplasty
The study team analyzed the rates, risk factors, and outcomes of AKI in 424 patients who underwent two-stage exchange arthroplasty with ALBC spacers and IV antibiotics for chronically infected knee replacements. The patients were managed at the Mayo Clinic between 2000 and 2017. 15% of patients had pre-existing CKD before surgery.
Advertisement
Thus the pre-existing chronic kidney disease (CKD) and high doses of antibiotics in bone cement expose the patients to an even higher risk of AKI. The devastating complication of failed total knee arthroplasty is deep, periprosthetic joint infections.
Advertisement
Several risk factors for AKI, including high doses of antibiotics used in the ALBC spacers (especially the commonly used antibiotics vancomycin and aminoglycoside ), high blood pressure, low blood volume, and atrial fibrillation (a heart rhythm disorder) were also identified by the study.
Most patients who developed AKI regained kidney function. However, at an average of 6 years postoperatively, eight patients had developed CKD while four were on dialysis.
Acute kidney injury is a relatively common complication of many medical conditions and procedures, including orthopedic surgery and heart surgery. The study provides new evidence on AKI in a large series of patients treated for infected total knee replacements at a single medical center.
The team thereby emphasizes the importance of screening to identify patients with possible decreases in kidney function before two-stage exchange arthroplasty. Also, the risk of AKI is related to pre-existing CKD and toxicity from ALBC spacers and IV antibiotics.
Source-Medindia