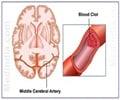
Researchers at MIT and San Camillo Hospital in Venice, Italy have said that motor impairments in stroke patients could actually be injuries
Researchers at MIT and San Camillo Hospital in Venice, Italy have said that motor impairments in stroke patients could actually be injuries in specific combination of muscle activity, known as synergies, which could help in the treatment of people suffering from stroke.
Earlier researchers have shown that groups of muscles tend to be co-activated as a unit in predicable patterns, or synergies, across a wide range of movements.The synergies are thought to represent the fundamental building blocks from which the brain constructs complex movements.
The new findings support this concept and also suggest new approaches to the rehabilitation of stroke patients.
Led by Emilio Bizzi, an MIT Institute Professor and a member of the McGovern Institute for Brain Research and the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, the researchers used electromyographic (EMG) recording to measure activity in arm and shoulder muscles of eight stroke patients as they performed a variety of reaching movements.
The patients had stroke damage in one cortical hemisphere only, so one arm was impaired while the other was largely unaffected.
The researchers used computational methods to identify groups of muscles whose activation was correlated across movements.
Advertisement
The results add weight to the view that the synergies are encoded in the brainstem or spinal cord, areas that were unaffected in these patients.
Advertisement
The findings suggest a new approach to the rehabilitation of stroke patients.
By identifying synergies whose activations are affected following a stroke, it may be possible to develop focused rehabilitation methods that specifically train the impaired synergies.
As a first step toward this goal, the researchers plan to monitor a group of stroke patients as they undergo rehabilitation therapy, to determine whether the post-stroke improvements in motor function can be explained as changes in the activation pattern of specific synergies.
Source-ANI
RAS