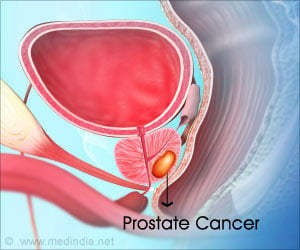
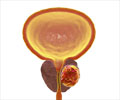
Surgical treatment caused steepest decline in sexual function and urinary incontinence and radiation therapy resulted in decline in bowel function.
‘Prostate cancer patients who underwent robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (RALP) had a better return of sexual function compared to any other treatment modality at 24 months post-therapy.’





"We hope our patient-reported outcomes and the comprehensive data collection in this cancer registry study will not only shed light on better patient counseling and care, but also better tracking of outcomes measurements in today's healthcare climate," said Dr. Gary Chien, lead author of the BJU International study.Source-Eurekalert

![Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA] & Prostate Cancer Diagnosis Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA] & Prostate Cancer Diagnosis](https://images.medindia.net/patientinfo/120_100/prostate-specific-antigen.jpg)