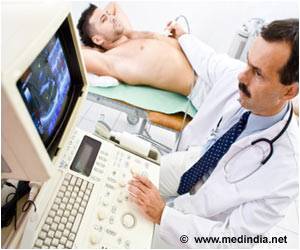
Ultrasound is an effective method that can reveal brachial plexus piercing variations in individuals diagnosed with nTOS symptoms.
‘Clinicians can now easily diagnose cases of nTOS with ultrasound along with patient history and symptoms.’





Despite its prevalence, this condition is notoriously difficult to diagnose in the clinical setting. However, researchers from Midwestern University have recently discovered a previously unknown cause of nTOS and an effective method of identifying it in patients.Heather F. Smith, Ph.D., Director of Anatomical Laboratories, and Sean Reeder, D.O., Associate Dean, representing the Arizona College of Osteopathic Medicine (AZCOM) at Midwestern University, are currently studying how anatomical variations in neck musculature and nerve pathways may contribute to nTOS, and investigating the utility of ultrasound to diagnose such variations.
Along with their team of Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine scholars, Vanessa Leonhard and Gregory Caldwell, and third-year AZCOM student Mei Goh, they have discovered anatomical variations that are linked with nTOS.
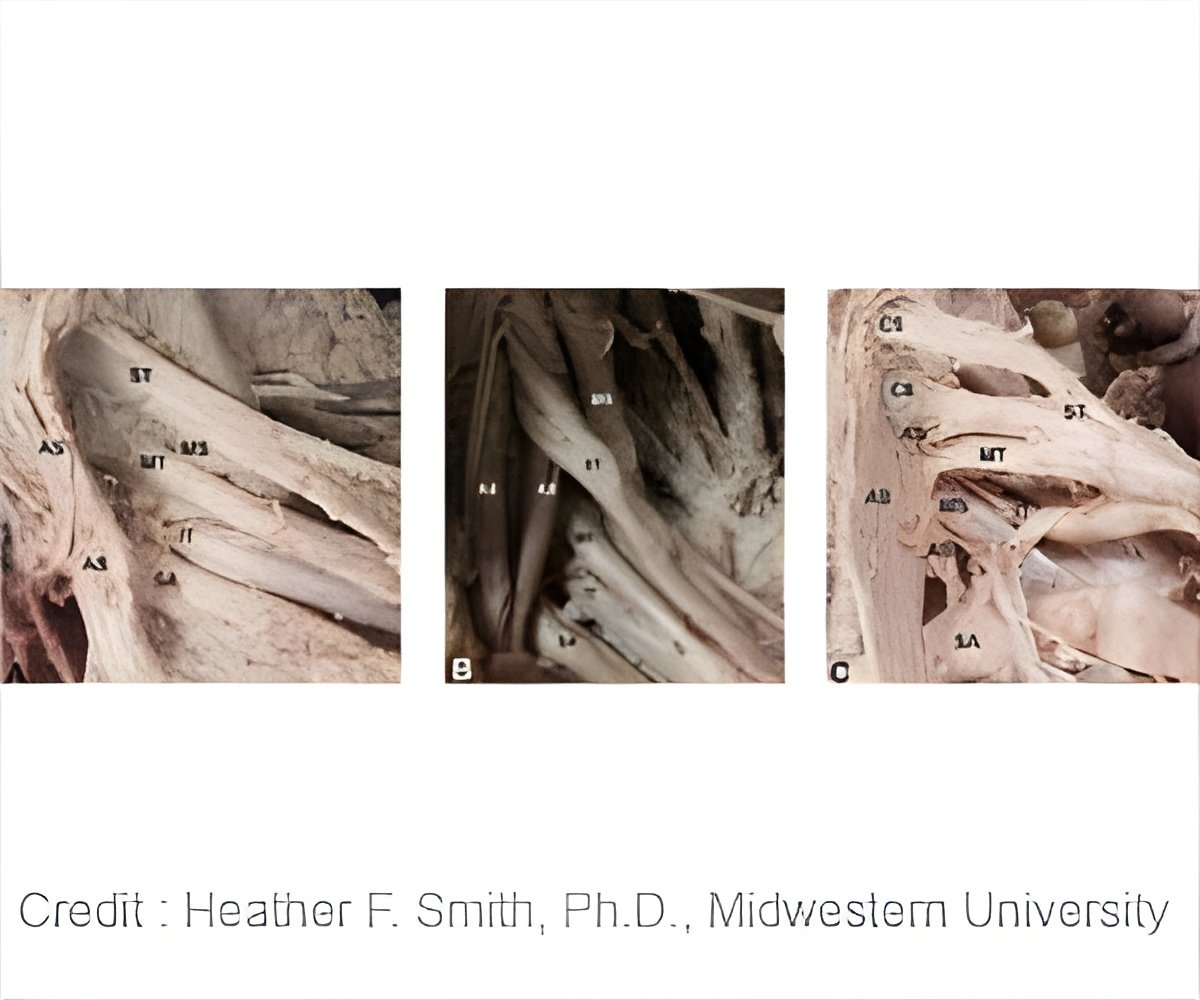
The classic understanding of the anatomy of this region is that the nerves of the brachial plexus travel between the scalene (neck) muscles without impingement on their way out to the arm, and traditional tests for diagnosing nTOS presume this pattern.
However, these researchers have discovered that parts of the brachial plexus often pierce the anterior scalene muscle belly and travel through it, resulting in neurologic impingement of the nerves by the muscle fibers and potential predisposition for nTOS symptoms.
Advertisement
To determine whether these variations were significantly correlated with nTOS symptoms, they recruited a sample of volunteer subjects who filled out a detailed questionnaire describing any neurogenic neck or arm symptoms they had, including those typically found in nTOS, and subjected them to traditional nTOS diagnostic positional testing.
Advertisement
These findings have important implications for the diagnosis and treatment of nTOS, and reveal a previously unknown explanation as to why nTOS has historically been difficult to diagnose. This study also demonstrates that ultrasound can help clinicians diagnose cases of nTOS caused by these anatomical variations, in conjunction with patient history and symptoms.
These findings were reported in the journal Diagnostics, in a special issue dedicated to the diagnosis and treatment of thoracic outlet syndrome.
Source-Eurekalert