‘Minimally invasive ultrasound-guided carpal tunnel release (UGCTR) can be used as an effective alternative to open or endoscopic surgery. The system shows long-term efficacy as it improves function and discomfort in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome.’
Read More..




The researchers wanted to evaluate the long term efficacy of UGCTR in improving function and discomfort in carpal tunnel syndrome patients. Read More..
The researchers reviewed sixty-one UGCTR procedures performed in 46 patients (25 women and 21 men; mean age 60.6 years) with clinically diagnosed carpal tunnel syndrome.
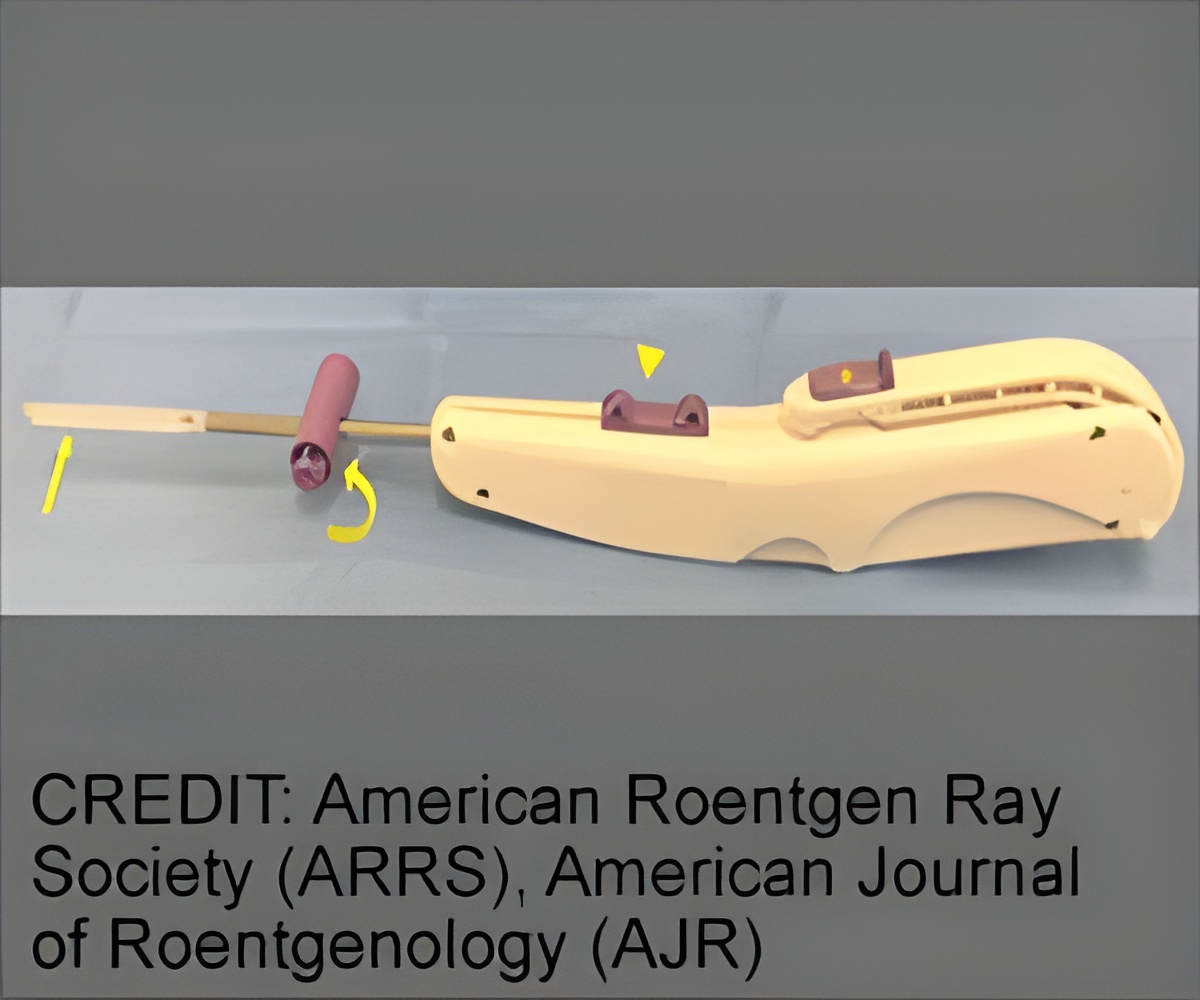
All procedures were alsp performed under local anesthetic at an outpatient radiology office using the SX-One MicroKnife® (Sonex Health).
"Patients answered three questionnaires (Quick-Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand [QDASH] and two parts of the Boston Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Questionnaire: symptom severity [BCTSQ-SS] and functional status [BCTSQ-FS] scales) assessing the affected wrist's function and discomfort immediately pre-procedure, 2 weeks post-procedure, and at least one year post-procedure," said first author Sarah I. Kamel.
The median pre-procedure scores were:
- 45.4 – QDASH
- 3.2 - BCTSQ-SS
- 2.5 - BCTSQ-FS
- 22.5 – QDASH
- 1.7 - BCTSQ-SS
- 1.9 - BCTSQ-FS
Advertisement
At long-term follow-up, 96% (52/54) of wrists demonstrated lower QDASH, and 98% (53/54) lower BCTSQ (average of BCTSQ-SS and BCTSQ-FS), vs pre-procedure scores.
Advertisement
The procedure includes a more extensive pre-procedural cleaning. It extends to the forearm circumferentially prior to draping.
A TegadermTM is now placed at the distal third of the forearm. It acts as an additional sterile barrier at the edge of the sterile field.
Two passes of the ligament transection are also performed routinely on patients in order to potentially reduce the risk of remnant tissue that may contribute to incomplete release.
Source-Medindia