Researchers from Mayo Clinic have been able to find out subtle changes in the motions of the heart that might improve the knowledge of heart function
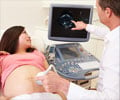
Researchers from Mayo Clinic have been able to find out subtle changes in the motions of the heart that might improve the knowledge of heart function by using the ultrasounds. They report that in this way it is also possible to predict the onset o heart damages like the heart attacks.
The researchers also feel that their study could also contribute to optimal adjustment of cardiac pacemakers or perhaps better design of artificial hearts. The findings, published in the current Journal of Applied Physiology, are based on “snapshots” of the mechanical transitions that occur between the main relaxation and contraction phases of the heartbeat. During these split-second transitions, the heart muscle “shifts gears” or prepares for the upcoming phase.Researchers at the Mayo Clinic Translational Ultrasound Research Unit study the mechanical, biochemical and electrical aspects of these transitions which occur between phases of relaxation -- when the heart ventricles fill with a volume of blood -- and contraction -- when the heart ejects most of the blood volume into body circulation.
Recently advanced, high-resolution ultrasound tissue Doppler imaging allowed them to experimentally measure these transitional tissue deformations, which last only milliseconds and are unnoticeable to the human eye. The technology allows slow-motion comparisons of these events separately between the inner and outer layers of the cardiac left ventricle. The researchers’ published measurements demonstrate how a rapid succession of motions occurring within tissue of the ventricular wall can appear chaotic if not observed closely and with high temporal resolution. The data also show how these transitions “reorganize” the ventricle to best perform its cycles of filling and ejection.
Alterations in the cardiac mechanical transitions detected by ultrasound imaging can be used as early indicators to predict heart problems, without the risk of an invasive procedure. Such an early warning system could allow physicians to intervene with appropriate therapies and thus prevent problems that could lead to heart attack or heart failure. The knowledge may also help researchers to develop new and targeted treatments in some heart diseases or further improve cardiac pacemakers or artificial hearts.
Source: Newswise
Medindia on Heart Attack: Further information
Heart attack: Also called myocardial infarction, coronary thrombosis or coronary occlusion, heart attack happens when the blood flow to the heart gets severely reduced or stopped altogether. Often heart attack is the direct result of formation of plaques on the blood vessels in a condition called atherosclerosis.