How does urinary incontinence affect your overall health? It can cause skin rashes, kidney damage, and mental health issues like anxiety and depression.
- Urinary incontinence can lead to skin infections, UTIs, and kidney damage
- Women and older adults are more likely to suffer from urinary incontinence
- Treatments include Kegel exercises, maintaining a healthy weight, and reducing caffeine and alcohol intake
Incontinence: Symptoms & Treatment - Urology Care Foundation
Go to source).
Up to 45% of women and 15% of men in India suffer from urinary incontinence, highlighting the importance of awareness and treatment for this common condition. #healthawareness #urinaryincontinence #medindia ’
What is Urinary Incontinence?
Urinary incontinence is an involuntary loss of bladder control that results in the inadvertent spilling of urine. It is a common condition that can range from infrequent minor leaks to more frequent and serious problems (2✔ ✔Trusted SourceUrinary Incontinence
Go to source).
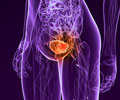
Urinary Incontinence Can Cause Skin, Kindey and Mental Health Issues
"The combination of hormones and stretched muscles weakens the muscles that control your bladder." This can result in an unintentional urine leak," said Dr. Ashwin Mallya, Consultant, Urologist and Robotic, Uro Onco Surgeon at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital. "Urinary incontinence affects not only the bladder but also the skin, causing rashes and infections due to the continual dampness. It can also cause urinary tract infections (UTIs) and, in severe cases, kidney damage," he noted.The doctor stated that it can also cause mental health issues such as "anxiety, depression, and social isolation." Many people may begin to avoid social activities or circumstances that make them feel embarrassed, which can lead to social isolation and a lower quality of life."
Women and Older Adults Are More Likely to Suffer from Urinary Incontinence
The illness can affect people of any age, but it is more common in older adults, particularly women during pregnancy and childbirth.The health expert stated that if it persists in women after childbirth or without childbirth, it is a cause for concern that must be addressed.
Dr. Arif Akhtar, Senior Consultant - Urology at Marengo Asia Hospital in Gurugram, told IANS that bladder control deteriorates with age due to weaker pelvic floor muscles and excessive or insufficient bladder muscle activity, causing the condition.
Causes of Urinary Incontinence
"Stress incontinence can be caused by pelvic muscle stretching and increased bladder pressure during pregnancy and childbirth. Menopause-induced estrogen decrease causes reduced urethral closure pressure and urogenital atrophy. Male overflow incontinence can be caused by both benign prostatic hyperplasia and complications from a prostatectomy.According to studies, up to 45% of women and 15% of men in India suffer from urine incontinence. This differential stems mostly from differences in anatomy, pregnancy, delivery, and menopause, all of which are specific risk factors for women.
Treatment of Urinary Incontinence
"Pelvic Floor Muscle Training (PFMT) with Kegel exercises and therapies to strengthen pelvic muscles are just a few of the many strategies used to prevent urinary incontinence," said Dr. Arif.Other approaches include adopting a healthy lifestyle, such as maintaining a healthy weight to reduce bladder pressure, staying active by exercising regularly to strengthen pelvic floor muscles, limiting caffeine and alcohol, which can irritate the bladder, and quitting smoking, which can cause coughing, which exacerbates stress incontinence, according to the doctors (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Management of urinary incontinence
Go to source).
References:
- Incontinence: Symptoms & Treatment - Urology Care Foundation - (https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/u/urinary-incontinence)
- Urinary Incontinence - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559095/)
- Management of urinary incontinence - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22876096/)
Source-Medindia