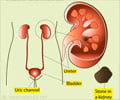
Urinary tract infection (UTI) risk can be reduced by drinking plenty of water. Drinking more fluids increases the rate of flushing of bacteria from the bladder.

‘Drinking more water increases the rate of flushing of bacteria from the bladder and reduces the concentration of bacteria in the bladder.’





"While doctors have long assumed this is the case and often recommended that women at risk for UTIs increase their fluid intake, it's never really undergone a prospective trial before," said Thomas M. Hooton, MD, lead author of the study and clinical director of the Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Miami School of Medicine. "It's good to know the recommendation is valid, and that drinking water is an easy and safe way to prevent an uncomfortable and annoying infection."Women are more likely to get UTIs than men in part because the urethra is shorter, meaning it is easier for bacteria to travel from the rectum and vagina to the bladder. Drinking more fluids increases the rate of flushing of bacteria from the bladder and also likely reduces the concentration of bacteria that enter the bladder from the vagina. This reduces the opportunities for bacteria to attach to cells that line the urinary tract, which is necessary to cause an infection, Dr. Hooton said.
The study included 140 healthy premenopausal women who had at least three UTIs in the last year and reported low daily fluid intake. Half of the women (70) who served as the control group continued their usual daily fluid intake, while the remainder were told to drink 1.5 liters of water a day (about three 16-ounce glasses) in addition to their usual daily fluid intake. After one year, women in the control group had 3.1 UTIs on average, whereas those in the water group had 1.6 UTIs on average, a 48 percent reduction. As a result, the water group averaged fewer regimens of antibiotics (1.8) than the limited-water group (3.5), a reduction of 47 percent. Reducing the use of antibiotics helps decrease the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Researchers followed the women throughout the year using visits and telephone calls. They documented that over the course of the study, on average women in the water group increased their daily water intake by 1.15 liters (about 2-1/2 pints) for a total daily fluid intake (including water and other beverages) of 2.8 liters, whereas women in the control group did not increase the amount of water they drank and had a total daily fluid intake of 1.2 liters.
"If a woman has recurrent UTIs and is looking for a way to reduce her risk, the evidence suggests that if she increases the amount of water she drinks and stays with it, she'll likely benefit," Dr. Hooton said.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert