Urine tests may be as efficient as the smear test at detecting high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) virus which is a huge risk factor for cervical cancer.
‘Women who avoid smear screening as they find it embarrassing or uncomfortable can now provide a urine sample instead to diagnose cervical cancer risk. Women are more likely to get the test done when it is non-intrusive and can be done at home.’
Read More..




The research was supported by the Manchester NIHR Biomedical Research Centre. Read More..
Urine testing could also have a role in the developing world, where cervical cancer is up to 15 times more common and smear testing largely non-existent.
The NHS cervical screening programme tests for so-called ’high-risk’ types of human papillomavirus (HPV) and the health of the cells of the cervix in women who test high-risk HPV positive.
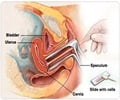
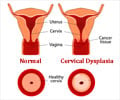
Around 1 in 20 women show abnormal changes which might go on to become cancer and are referred for colposcopy, where the cervix is examined under magnification, allowing abnormal areas to be seen, sampled and treated, before they ever cause cancer.
According to the team, cervical smear samples, self-collected vaginal samples, and urine samples are all effective at picking up a high-risk HPV infection.
Advertisement
"We’re really very excited by this study, which we think has the potential to significantly increase participation rates for cervical cancer screening in a key demographic group," said Dr. Emma Crosbie.
Advertisement
She added: "Campaigns to encourage women to attend cervical screening have helped. The brilliant campaign by the late Jade Goody increased numbers attendance by around 400,000 women.
"But sadly, the effects aren’t long lasting, and participation rates tend to fall back after a while. We clearly need a more sustainable solution."
Of the 100 or so types of HPV, some are linked to cervical cancer, and some are linked to other conditions, like genital warts.
Most cervical cancers are caused by high-risk types HPV-16 and HPV-18.
104 women attending the colposcopy clinic at St Mary’s Hospital, Manchester participated in the study and were screened using two brands of HPV testing kits.
Around two-thirds of the women tested positive for any high-risk HPV type, and a third for HPV-16 or HPV-18.
From the total, eighteen women had pre-cancerous changes to the cervix that needed treatment.
With the Roche HPV testing kit, urine, vaginal self samples, and cervical smears picked up 15 of these.
With the Abbott HPV testing kit, urine picked up 15 of these and vaginal self samples and cervical smears picked up 16.
Dr. Crosbie said: "These results provide exciting proof of principle that urine HPV testing can pick up cervical pre-cancer cells, but we need to trial it on a greater number of women before it can be used in the NHS. We hope that is going to happen soon.
"Urine is very simple to collect, and most hospitals in the developed and developing world have access to the lab equipment to process and test the samples.
"Let us hope this is a new chapter in our fight against cervical cancer, a devastating and pernicious disease."
Source-Eurekalert