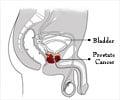
Consumption of supplemental zinc is associated with an increased risk of advanced prostate cancer, according to an analysis of data from the Health
Consumption of supplemental zinc is associated with an increased risk of advanced prostate cancer, according to an analysis of data from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study.
The prostate has higher concentrations of zinc than do other soft tissues. However, studies of the effect of zinc on prostate cancer risk have been inconclusive.Among more than 46,000 men followed in the health professionals study, there were 2901 documented cases of prostate cancer during 14 years of follow-up, including 434 cases that were advanced at diagnosis.
Adjustment for the same variables also showed a 2.37-fold increased relative risk of advanced prostate cancer for men who used zinc supplements for 10 years or more (p < 0.001).
Despite the lack of a robust explanation for the described association, findings suggest that the role of chronic oversupply of zinc in prostate carcinogenesis requires further investigation say researchers.

![Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA] Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA]](https://www.medindia.net/images/common/patientinfo/120_100/prostate-specific-antigen.jpg)