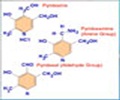
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient for the body. The body cannot produce vitamin B12, so it is vital to consume adequate levels to lead a healthy life.

Vitamin B12 has essential functions in the body.
- Aids in formation of red blood cells (RBCs). Prevents a type of anemia known as megaloblastic anemia, which makes people weak and tired
- Helps to keep brain and nerves healthy
- Strengthens the immune system
- Improves the health of the heart by reducing an amino acid, homocysteine. Homocysteine is linked to an increased risk of heart disease
- Helps reduce depression by manufacturing serotonin, a mood-enhancing chemical
- Prevent age related macular degeneration
- Reduces risk of birth defects and plays a key role in healthy pregnancy
- Supports bone health
- Energy booster
- Promotes healthy skin, nails and hair
- Constipation
- Weight loss
- Weakness and fatigue
- Increase in heart rate
- Pale looking skin
- Reduced appetite
- Shortness of breath
- Megaloblastic anemia
- Mouth ulcers and glossitis
- Blurry vision
- Nerve issues
- Confusion
- Mood changes and depression
‘Vitamin B12 is vital to keep the body healthy. It is essential to consume vitamin-rich foods to maintain adequate levels of vitamin B12 to avoid vitamin B12 deficiency problems.’
Read More..




Vitamin B12 deficiency can generally be avoided by eating healthy. However, some people are at a higher risk.
Read More..
- Elders
- Diabetic people under metformin drug
- Weight loss surgery patients
- People with strict vegan diet
- People taking medications for Crohn’s disease
Animal foods are rich in vitamin B12.
- Eggs
- Poultry
- Fish
- Beef liver
- Dairy products
Check the label of the food to know if the food contains fortified vitamin B12.
Recommended Levels of Vitamin B12
Number of factors such as age, eating habits and health conditions play a role in determining the amount of vitamin B12 required daily.
Advertisement
Vitamin B12 can interact with certain medications like chloramphenicol, metformin, vitamin C supplements, aminosalicylic acid etc.
Advertisement
Overall, vitamin B12 is key nutrient that maintains many crucial functions in the body. It is necessary to make sure the adequate amount of vitamin B12 is consumed.
Source-Medindia