Consuming diet that are rich in vitamin C may help to curb the harmful effects of air pollution for those suffering from chronic lung diseases.

"This study adds to a small but growing body of evidence that the effects of air pollution might be modified by antioxidants," said Michael Brauer, an environmental health scientist at the University of British Columbia in Canada.
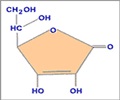
Antioxidants, such as vitamin C, may protect the body from harmful molecules called free radicals that damage cells. Free radicals can form when air pollution enters the lungs, and evidence suggests they play a role in heart disease, cancer and even respiratory ailments.
Antioxidants can bind to free radicals, counteracting them before they damage cells.
In the new study, researchers at Imperial College in London looked at more than 200 patients admitted to the hospital for asthma or COPD, along with the levels of air pollution on the days before and after they entered the hospital. The majority of patients were between ages 54 and 74, though some were as young as 18. Many of them were former smokers.
Specifically, the researchers looked at levels of "course particulate matter," which is produced largely through the combustion of fossil fuels.
Advertisement
However, the risk of admission was 1.2 times greater among people with low levels of vitamin C.
Advertisement
The study is published in the July issue of the journal Epidemiology.
Source-ANI