Vitamin D deficiency in expectant mothers affects the social development and motor skills of children in their early years of life.

‘Sufficient amounts of Vitamin D reduces the risk of osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.’





Tests included assessments of their coordination, such as kicking a ball, balancing and jumping and their usage of fine muscles, including holding a pencil and building a tower with bricks. The study was published in the British Journal of Nutrition.Vitamin D insufficiency in pregnancy was also found to affect a child's social development at age 3½ years.However, no associations were found between maternal vitamin D status and other outcomes at older ages (IQ and reading ability at 7 to 9 years old).
Previous evidence from animal studies has shown that the neurocognitive development of foetuses is detrimentally affected when levels of vitamin D in the mothers are low. Researchers believe that interactions between vitamin D and dopamine in the brain of the foetus may play a crucial role in the neurological development of brain areas controlling motor and social development.
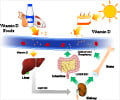
In addition to the ground-breaking findings in this study, vitamin D, which is derived from sunlight and diet, is also proven to regulate the amount of calcium and phosphate in the body, which is vital in reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
Sufficient vitamin D may also be associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, infectious and autoimmune disease and diabetes.
Advertisement
"Vitamin D is found in oily fish (e.g. salmon, sardines, mackerel and fresh tuna) and in small amounts of red meat, eggs, fortified fat spreads and some breakfast cereals. However, unless a large portion of oily fish (100g) is eaten daily it is difficult to get the recommended daily intake of 10 micrograms per day from food alone.
Advertisement
"However, it is important to remember that 'more is not necessarily better' and it is important not to take too much vitamin D from supplements as it can be toxic in very high doses".
Source-Eurekalert