Bladder cancer is the ninth most common cancer in the world. Vitamin D deficiency can increase the risk of bladder cancer, finds a new study.
Highlights
- Individuals with vitamin D deficiency are at greater risk of developing bladder cancer.
- Lack of vitamin D may prevent the bladder cells from stimulating an adequate response to abnormal cells.
- Higher levels of vitamin D can improve cancer survival and outcomes
Link Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Risk of Bladder Cancer
Researchers from the University of Warwick and University Hospital Coventry and Warwickshire reviewed seven studies to investigate the link between vitamin D and risk of bladder cancer. The number of participants involved in the various studies ranged from 112 to 1125. Five studies linked vitamin D deficiency to an increased risk of bladder cancer.The researchers also looked at the cells that line the bladder called as transitional epithelial cells, to study cancer risk. The researchers found that the transitional epithelial cells activate and respond to vitamin D to stimulate an immune response.
Dr Rosemary Bland, the lead author of the study, said that immune system might have a role in cancer prevention by targeting abnormal cells before they become cancerous.
"More clinical studies are required to test this association, but our work suggests that low levels of vitamin D in the blood may prevent the cells within the bladder from stimulating an adequate response to abnormal cells," said Dr Bland.
"As vitamin D is cheap and safe, its potential use in cancer prevention is exciting and could potentially impact on the lives of many people."
The systemic review was presented at the Society for Endocrinology annual conference in Brighton.
Vitamin D Deficiency
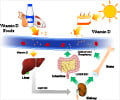
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, naturally found in foods. This sunshine vitamin helps the body to control calcium and phosphate levels. Studies conducted earlier have linked vitamin D deficiency with cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disease, cancer and cognitive impairment. Common food sources of Vitamin D include fatty fish (tuna, mackerel, and salmon), egg yolk, beef liver, fortified cereals, dairy and orange juice.The recommended daily allowance (RDA) of vitamin D is 600 IU for those 1-70 years of age and pregnant or lactating women. For older people over 71 years of age, RDA of vitamin D is 800 IU.
- Over a billion of people suffer from vitamin D deficiency.
- The black and Hispanic are vitamin D deficient in the United States
- About 13 percent of women and nine percent of men in the UK are vitamin D deficient
- One in five adults in the UK is vitamin D deficient
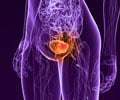
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer begins when the cells lining the bladder start to grow uncontrollably. The three types of bladder cancer are transitional cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Smoking is one of the major risk factors for bladder cancer. Exposure to industrial chemicals is another cause of bladder cancer.
Facts
- Bladder cancer is the ninth most common cancer
- About 430,000 new cases of bladder cancer were diagnosed in 2012
- Fifth most commonly diagnosed cancer in the United States
- In 2016, more than 77,000 Americans will be diagnosed with bladder cancer
- Bladder cancer is the seventh most common cancer in the United Kingdom
- About 10,000 people are diagnosed with bladder cancer every year in the UK
- More than one million Indians are diagnosed with bladder cancer every year
- Nine out of 10 people with bladder cancer are over the age of 55
- Men are four more likely to get bladder cancer than women
- Bladder cancer statistics - (http://www.wcrf.org/int/cancer-facts-figures/data-specific-cancers/bladder-cancer-statistics)
- Bladder Cancer—Patient Version - (https://www.cancer.gov/types/bladder)
- Bladder Cancer Risk Factors - (http://www.cancer.org/cancer/bladdercancer/detailedguide/bladder-cancer-risk-factors)
- Vitamin D Deficiency- An Ignored Epidemic - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3068797/)
- Vitamin D Status: United States, 2001–2006 - (http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db59.htm)